Page 311 - Process Modelling and Simulation With Finite Element Methods
P. 311
298 Process Modelling and Simulation with Finite Element Methods
interface after the merging of two drops. In coalescence phenomena, the contact
point between interfaces of two drops is very important and hence the approach
of two drops is treated by various means in this computational study and is
described in detail in following sections.
8.4.1 Coalescence of two axisymmetric drops
The simplest way to start the numerical simulation is to assume a symmetrical 2-
D domain, which would significantly reduce the computational time. The system
can be physically described as a rectangular domain with one boundary acting as
an axis of symmetry and all other boundaries are insulated. Two equally sized
drops are initially separated by axial distance equal to two times their diameter.
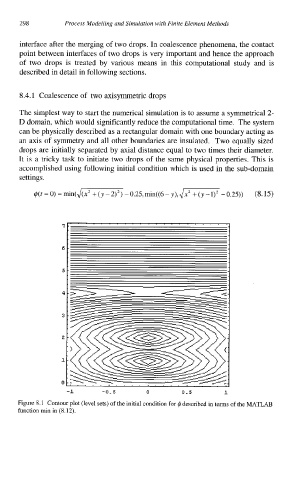
It is a tricky task to initiate two drops of the same physical properties. This is
accomplished using following initial condition which is used in the sub-domain
settings.
$(f =0) = rnin(,/~-0.25,min((6-y),~~-0.25)) (8.15)
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1
Figure 8.1 Contour plot (level sets) of the initial condition for 4 described in terms of the MATLAB
function min in (8.12).