Page 227 - Psychological Management of Individual Performance
P. 227
demands influence performance 211
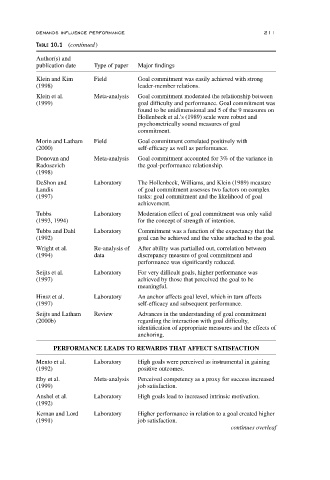
TABLE 10.1 (continued)
Author(s) and
publication date Type of paper Major findings
Klein and Kim Field Goal commitment was easily achieved with strong
(1998) leader-member relations.
Klein et al. Meta-analysis Goal commitment moderated the relationship between
(1999) goal difficulty and performance. Goal commitment was
found to be unidimensional and 5 of the 9 measures on
Hollenbeck et al.’s (1989) scale were robust and
psychometrically sound measures of goal
commitment.
Morin and Latham Field Goal commitment correlated positively with
(2000) self-efficacy as well as performance.
Donovan and Meta-analysis Goal commitment accounted for 3% of the variance in
Radosevich the goal-performance relationship.
(1998)
DeShon and Laboratory The Hollenbeck, Williams, and Klein (1989) measure
Landis of goal commitment assesses two factors on complex
(1997) tasks: goal commitment and the likelihood of goal
achievement.
Tubbs Laboratory Moderation effect of goal commitment was only valid
(1993, 1994) for the concept of strength of intention.
Tubbs and Dahl Laboratory Commitment was a function of the expectancy that the
(1992) goal can be achieved and the value attached to the goal.
Wright et al. Re-analysis of After ability was partialled out, correlation between
(1994) data discrepancy measure of goal commitment and
performance was significantly reduced.
Seijts et al. Laboratory For very difficult goals, higher performance was
(1997) achieved by those that perceived the goal to be
meaningful.
Hinsz et al. Laboratory An anchor affects goal level, which in turn affects
(1997) self-efficacy and subsequent performance.
Seijts and Latham Review Advances in the understanding of goal commitment
(2000b) regarding the interaction with goal difficulty,
identification of appropriate measures and the effects of
anchoring.
PERFORMANCE LEADS TO REWARDS THAT AFFECT SATISFACTION
Mento et al. Laboratory High goals were perceived as instrumental in gaining
(1992) positive outcomes.
Eby et al. Meta-analysis Perceived competency as a proxy for success increased
(1999) job satisfaction.
Anshel et al. Laboratory High goals lead to increased intrinsic motivation.
(1992)
Kernan and Lord Laboratory Higher performance in relation to a goal created higher
(1991) job satisfaction.
continues overleaf