Page 219 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 219
209 GYROTRON height-finder, nodding-beam
through multipath lobes of a 2D search radar antenna pattern,
from which a constant target altitude may be calculated.
(6) Measurement of relative amplitude or phase of target
echoes in two antennas displaced in altitude, leading to a
monopulse estimate of elevation angle.
Some types of height finders are described below. (See also
RADAR, ‘3D.) DKB
The nodding-beam height finder is the specialized radar (1)
in the basic height-finding methods. A 2D search radar main-
tains surveillance over the volume of interest, detecting tar-
gets and measuring their ranges and azimuth angles. Upon
detection and establishment of a track on a new target, a
Figure G4 Types of gyrotron amplifier configurations (from
Ewell, 1981, Fig. 2-44, p. 79, reprinted by permission of request is sent to the height finder for elevation measurement.
McGraw-Hill). The height finder slews its antenna to the azimuth designated
by the search radar and performs a scan over an elevation sec-
tor appropriate to the range designated by the 2D radar. Target
.
echoes are displayed on a range-height indicator (RHI), and
Table G1 elevation angle q is measured by an operator or an angle-gate
t
Peak Power Levels from Cyclotron Masers Driven by Intense circuit. Range R is also measured to an accuracy better than
Relativistic Electron Beams that provided by the search radar. The target height above the
horizontal plane at the radar site is then calculated as
Peak Accelerating
Wavelength Diode h = R sin q
microwave voltage t t
(cm) current (kA) This height is corrected as necessary for site altitude, atmo-
power (MW) (MV)
spheric refraction, and curvature of Earth to give target alti-
4.0 900 3.3 80
tude above sea level, as needed for ground-controlled
2.0 350 2.6 40 intercept of the target by a fighter aircraft. A typical nodding-
0.8 8 0.6 15 beam height finder is shown in Fig. H1. The antenna is elon-
0.4 2 0.6 15 gated in the vertical direction to provide a narrow elevation
beam for accurate measurement, while the azimuth beam-
(from Ewell, 1981, p. 77, reprinted by permission of McGraw-Hill).
width is wide enough to accommodate errors in designation
from the search radar. DKB
Ref.: Skolnik (1990), p. 20.3.
H
HAMMING WINDOW (see WEIGHTING).
HEIGHT FINDER. Height finders are radars designed to
measure the elevation angle of targets in a surveillance sys-
tem, permitting target altitude to be calculated from measured
range. The methods by which elevation angle and hence alti-
tude is determined include:
(1) Assignment of a specialized radar that performs sec-
tor scan in elevation for measurement in that coordinate, on
targets designated by a 2D search radar.
(2) Search with a scanning-beam 3D radar, in which a
narrow beam is scanned over a raster covering both azimuth
and elevation and providing measurement of both angles,
along with range, on detected targets.
(3) Search with a stacked-beam 3D radar, in which multi-
ple beams cover the elevation sector as the antenna scans in
azimuth, providing monopulse measurement in elevation.
(4) Measurement of multipath time delay on targets
detected in a 2D search radar, such that target altitude may be
calculated from known target range, radar antenna altitude,
and multipath delay.
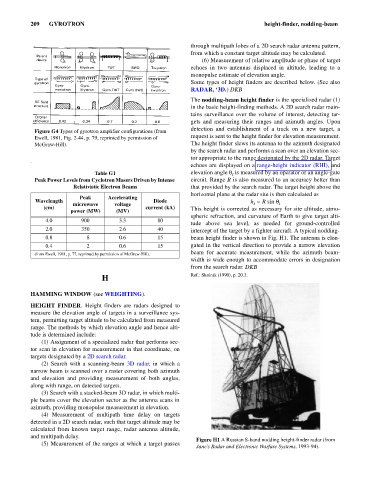
Figure H1 A Russian S-band nodding height-finder radar (from
(5) Measurement of the ranges at which a target passes
Jane’s Radar and Electronic Warfare Systems, 1993-94).