Page 299 - Radar Technology Encyclopedia
P. 299
289 NOMENCLATURE, radar NUCLEAR EFFECTS
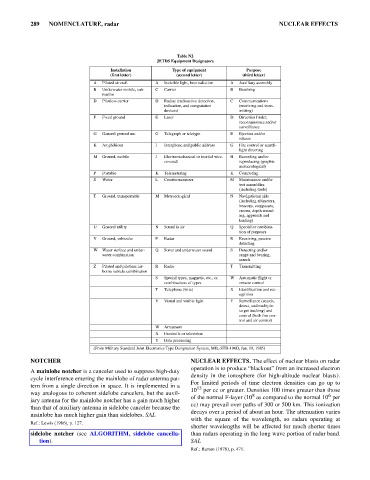
Table N2
JETDS Equipment Designators
Installation Type of equipment Purpose
(first letter) (second letter) (third letter)
A Piloted aircraft A Invisible light, heat radiation A Auxiliary assembly
B Underwater mobile, sub- C Carrier B Bombing
marine
D Pilotless carrier D Radiac (radioactive detection, C Communications
indication, and computation (receiving and trans-
devices) mitting)
F Fixed ground E Laser D Direction finder,
reconnaissance and/or
surveillance
G General ground use G Telegraph or teletype E Ejection and/or
release
K Amphibious I Interphone and public address G Fire control or search-
light directing
M Ground, mobile J Electromechanical or inertial wire- H Recording and/or
covered reproducing (graphic
meteorological)
P Portable K Telemetering K Computing
S Water L Countermeasures M Maintenance and/or
test assemblies
(including tools)
T Ground, transportable M Meteorological N Navigational aids
(including altimeters,
beacons, compasses,
racons, depth sound-
ing, approach and
landing)
U General utility N Sound in air Q Special or combina-
tion of purposes
V Ground, vehicular P Radar R Receiving, passive
detecting
W Water surface and under- Q Sonar and underwater sound S Detecting and/or
water combination range and bearing,
search
Z Piloted and pilotless air- R Radio T Transmitting
borne vehicle combination
S Special types, magnetic, etc., or W Automatic flight or
combinations of types remote control
T Telephone (wire) X Identification and rec-
ognition
V Visual and visible light Y Surveillance (search,
detect, and multiple-
target tracking) and
control (both fire con-
trol and air control)
W Armament
X Facsimile or television
Y Data processing
(From Military Standard Joint Electronics Type Designation System, MIL-STD-196D, Jan. 19, 1985)
NOTCHER NUCLEAR EFFECTS. The effect of nuclear blasts on radar
operation is to produce “blackout” from an increased electron
A mainlobe notcher is a canceler used to suppress high-duty
density in the ionosphere (for high-altitude nuclear blasts).
cycle interference entering the mainlobe of radar antenna pat-
For limited periods of time electron densities can go up to
tern from a single direction in space. It is implemented in a 13
10 per cc or greater. Densities 100 times greater than those
way analogous to coherent sidelobe cancelers, but the auxil- 8 6
of the normal F-layer (10 as compared to the normal 10 per
iary antenna for the mainlobe notcher has a gain much higher
cc) may prevail over paths of 300 or 500 km. This ionization
than that of auxiliary antenna in sidelobe canceler because the
decays over a period of about an hour. The attenuation varies
mainlobe has much higher gain than sidelobes. SAL
with the square of the wavelength, so radars operating at
Ref.: Lewis (1986), p. 127.
shorter wavelengths will be affected for much shorter times
sidelobe notcher (see ALGORITHM, sidelobe cancella- than radars operating in the long wave portion of radar band.
tion). SAL
Ref.: Barton (1976), p. 471.