Page 187 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 187
Radiation Effects on Matter 171
The absorbed dose (D) is the amount of radiation energy absorbed per unit mass:
O = dEabs/dm (7.8)
According to (7.1) Eab s =E in - Eou r The SI unit is the Gray (Gy)
1 Gy = 1J/kg
An old, still sometimes used, unit is the rad (for radiation _absorbed dose)
1 Gy = 100 rad
The dose rate is the absorbed dose per unit time. The SI unit is Gray per second (Gy/s).
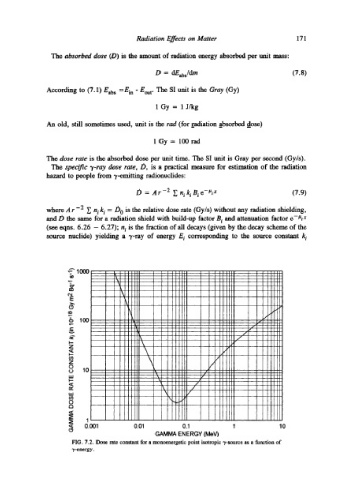
The specific "y-ray dose rate, D, is a practical measure for estimation of the radiation
hazard to people from T-emitting radionuclides:
D = A r -2 ~ ni ki Bi e-#~x (7.9)
where A r-2 ~ ni ki = Do is the relative dose rate (Gy/s) without any radiation shielding,
and D the same for a radiation shield with build-up factor B i and attenuation factor e-~'t x
(see eqns. 6.26 - 6.27); n i is the fraction of all decays (given by the decay scheme of the
source nuclide) yielding a "y-ray of energy E i corresponding to the source constant k i
~" 1000
%..
O"
El
(~
E
(9 |
q.-
lOO
q--
t-
~
I--
z
<
F-
z
0
0 10
UJ
i-
n-
uJ
c~
0
0
<
1 1ll
0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10
GAMMA ENERGY (MeV)
FIG. 7.2. Dose rate constant for a monoenergetic point isotropie "y-source as a function of
7-energy.