Page 280 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 280
264 Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry
(c) Ion exchange
The technique depends on the distribution of metal cations between a solid cation
exchange resin and an aqueous solution. The exchange process for the M z+ ion takes place
according to the equation
MZ+(aq) + zRH(resin) ~ MRz(resin ) + zH+(aq)
Kie x = ([MR z] [H] z )/([M] [RH] z ) (9.24.a)
omitting ionic charges and phase indices. Introducing Diex, from (9.7), in (9.24.a) gives
Die x = Kir x [RH] z [H] -z (9.24.b)
showing that Die x is a constant at constant solution/resin conditions (as in column ion
exchange separations). However, when used for determining equilibrium constants in a
system with several metal species in solution, each ionic species must be represented by an
equation of type (9.24.a), leading to rather complicated expressions.
9.4.4. Studies of surfaces and reactions in solids
Surface properties of solids have been studied by dipping specimens into a solution
containing a suitable radioactive tracer, and, after some "exposure time', removing them,
washing their surface carefully and measuring the radiation emitted from them. It has been
. I I I I I
,=
4.5
4.0
z 3.5
~m
3.0
2.s I I I I I "
-3.4 -3.0 -2.s -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -o.s
hog p4so i]
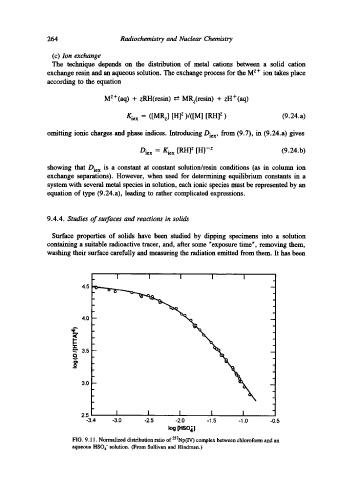
FIG. 9.11. Normalized distribution ratio of 237Np(IV) complex between chloroform and an
aqueous HSO 4" solution. (From Sullivan and Hindman.)