Page 114 - Rapid Learning in Robotics
P. 114
100 Application Examples in the Vision Domain
z L h i h i h i h z i hj nji hj oji h n oi hj u ji hj u ji
P P
PSOM range L L
4 and 8 points are input
150 2 2.6 3.1 2.9 0.11 0.039 0.046 0.0084 given given
150 2 2.7 3.2 2.8 0.12 0.043 0.048 0.0084 0.010 0.0081
Learn only rotational part
3 3 3 150 2.6 3.0 2.5 0.046 0.048 0.0074 0.018 0.012
4 4 4 150 0.63 1.2 0.93 0.021 0.019 0.0027 0.013 0.0063
5 5 5 150 0.12 0.12 0.094 0.0034 0.0027 0.00042 0.0017 0.00089
Various rotational ranges
90 1 0.64 0.56 0.53 0.034 0.0085 0.0082 0.00082 0.0036 0.0021
120 1 1.5 1.5 1.4 0.037 0.021 0.021 0.0032 0.0079 0.0049
150 1 2.7 3.2 2.8 0.077 0.044 0.048 0.0084 0.013 0.010
180 1 6.5 5.4 7.0 0.19 0.079 0.098 0.014 0.019 0.016
Various training set sizes
150 2 2.7 3.2 2.8 0.12 0.043 0.048 0.0084 0.010 0.0081
150 2 2.6 3.2 2.8 0.11 0.043 0.048 0.0084 0.0097 0.0077
150 2 0.49 0.97 0.73 0.12 0.018 0.016 0.0030 0.0089 0.0059
150 2 0.52 0.98 0.71 0.035 0.017 0.014 0.0026 0.0082 0.0053
150 2 0.14 0.13 0.14 0.024 0.0033 0.0030 0.00043 0.0018 0.0011
Shift depth range z
150 1..3 3.8 3.4 3.7 0.12 0.061 0.064 0.0083 0.049 0.025
150 2..4 2.6 3.2 2.8 0.11 0.043 0.048 0.0084 0.0097 0.0077
150 3..5 2.6 3.2 2.9 0.15 0.042 0.047 0.0084 0.0050 0.0045
Various distance ranges
150 2 2.6 3.2 2.8 0.11 0.043 0.048 0.0084 0.0097 0.0077
150 4 2.6 3.2 2.8 0.20 0.042 0.047 0.0084 0.0068 0.0059
150 6 2.6 3.2 2.9 0.36 0.043 0.048 0.0084 0.0057 0.0052
150 6 0.65 0.73 0.93 0.39 0.016 0.013 0.00047 0.0070 0.0051
150 6 0.44 0.43 0.60 0.14 0.0097 0.0083 0.00042 0.0043 0.0029
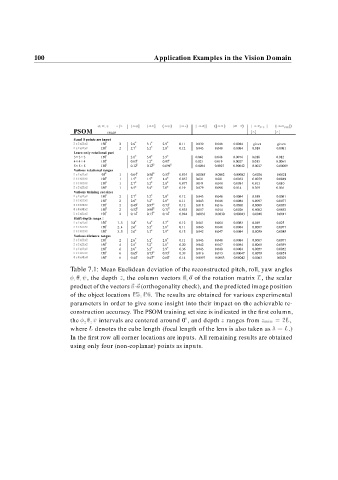
Table 7.1: Mean Euclidean deviation of the reconstructed pitch, roll, yaw angles
, the depth z, the column vectors n o of the rotation matrix T, the scalar
o
product of the vectors n (orthogonality check), and the predicted image position
of the object locations P . PThe results are obtained for various experimental
parameters in order to give some insight into their impact on the achievable re-
construction accuracy. The PSOM training set size is indicated in the first column,
the intervals are centered around 0 , and depth z ranges from z min L,
where L denotes the cube length (focal length of the lens is also taken as L.)
In the first row all corner locations are inputs. All remaining results are obtained
using only four (non-coplanar) points as inputs.