Page 87 - Rapid Learning in Robotics
P. 87
5.6 Continuity Aspects 73
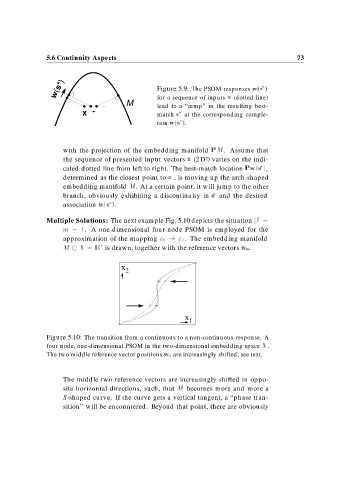
w(s*) . Figure 5.9: The PSOM responses w s
.
.
M for a sequence of inputs x (dotted line)
lead to a “jump” in the resulting best-
x match s at the corresponding comple-
tion w s .
with the projection of the embedding manifold PM. Assume that
the sequence of presented input vectors x (2 D!) varies on the indi-
cated dotted line from left to right. The best-match location Pw s ,
determined as the closest point to x , is moving up the arch-shaped
embedding manifold M. At a certain point, it will jump to the other
branch, obviously exhibiting a discontinuity in s and the desired
association w s .
Multiple Solutions: The next example Fig. 5.10 depicts the situation jIj
m . A one-dimensional four-node PSOM is employed for the
approximation of the mapping x x . The embedding manifold
M X R is drawn, together Iwith the reference vectors w a.
x
2
x
1
Figure 5.10: The transition from a continuous to a non-continuous response. A
four node, one-dimensional PSOM in the two-dimensional embedding space X.
The two middle reference vector positions w a are increasingly shifted, see text.
The middle two reference vectors are increasingly shifted in oppo-
site horizontal directions, such, that M becomes more and more a
S-shaped curve. If the curve gets a vertical tangent, a “phase tran-
sition” will be encountered. Beyond that point, there are obviously