Page 83 - Rapid Learning in Robotics
P. 83
5.3 Topological Order Introduces Model Bias 69
b) c)
1 2
x
a) 3 4
5
x 6
d) e)
1 2
x
x
3
4
5
6
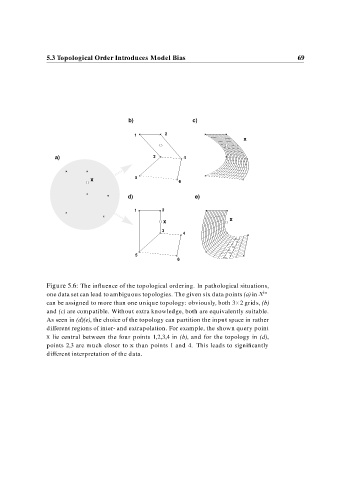
Figure 5.6: The influence of the topological ordering. In pathological situations,
one data set can lead to ambiguous topologies. The given six data points (a) in X in
can be assigned to more than one unique topology: obviously, both 3 2 grids, (b)
and (c) are compatible. Without extra knowledge, both are equivalently suitable.
As seen in (d)(e), the choice of the topology can partition the input space in rather
different regions of inter- and extrapolation. For example, the shown query point
x lie central between the four points 1,2,3,4 in (b), and for the topology in (d),
points 2,3 are much closer to x than points 1 and 4. This leads to significantly
different interpretation of the data.