Page 81 - Reciprocating Compressors Operation Maintenance
P. 81
68 Reciprocating Compressors: Operation and Maintenance
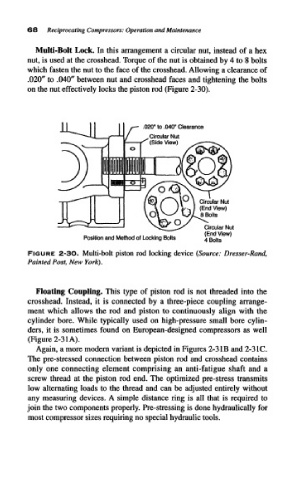
Multi-Bolt Lock. In this arrangement a circular nut, instead of a hex
nut, is used at the crosshead. Torque of the nut is obtained by 4 to 8 bolts
which fasten the nut to the face of the crosshead. Allowing a clearance of
.020" to .040" between nut and crosshead faces and tightening the bolts
on the nut effectively locks the piston rod (Figure 2-30).
.020" to .040" Clearance
Circular Nut
(End View)
Position and Method of Locking Bolts 4 Q 0 | ts
FIGURE 2-3O. Multi-bolt piston rod locking device (Source: Dresser-Rand,
Painted Post, New York).
Floating Coupling. This type of piston rod is not threaded into the
crosshead. Instead, it is connected by a three-piece coupling arrange-
ment which allows the rod and piston to continuously align with the
cylinder bore. While typically used on high-pressure small bore cylin-
ders, it is sometimes found on European-designed compressors as well
(Figure 2-31 A).
Again, a more modern variant is depicted in Figures 2-3IB and 2-31C.
The pre-stressed connection between piston rod and crosshead contains
only one connecting element comprising an anti-fatigue shaft and a
screw thread at the piston rod end. The optimized pre-stress transmits
low alternating loads to the thread and can be adjusted entirely without
any measuring devices. A simple distance ring is all that is required to
join the two components properly. Pre-stressing is done hydraulically for
most compressor sizes requiring no special hydraulic tools.