Page 229 - Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
P. 229
200 Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
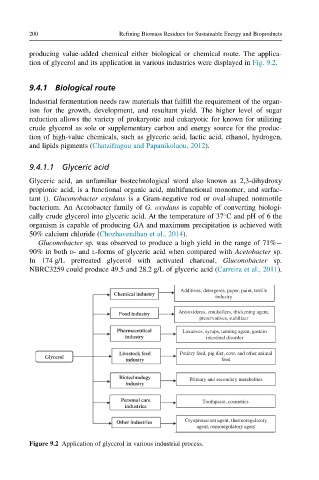
producing value-added chemical either biological or chemical route. The applica-
tion of glycerol and its application in various industries were displayed in Fig. 9.2.
9.4.1 Biological route
Industrial fermentation needs raw materials that fulfill the requirement of the organ-
ism for the growth, development, and resultant yield. The higher level of sugar
reduction allows the variety of prokaryotic and eukaryotic for known for utilizing
crude glycerol as sole or supplementary carbon and energy source for the produc-
tion of high-value chemicals, such as glyceric acid, lactic acid, ethanol, hydrogen,
and lipids pigments (Chatzifragou and Papanikolaou, 2012).
9.4.1.1 Glyceric acid
Glyceric acid, an unfamiliar biotechnological word also known as 2,3-dihydroxy
propionic acid, is a functional organic acid, multifunctional monomer, and surfac-
tant (). Gluconobacter oxydans is a Gram-negative rod or oval-shaped nonmotile
bacterium. An Acetobacter family of G. oxydans is capable of converting biologi-
cally crude glycerol into glyceric acid. At the temperature of 37 C and pH of 6 the
organism is capable of producing GA and maximum precipitation is achieved with
50% calcium chloride (Chozhavendhan et al., 2014).
Gluconobacter sp. was observed to produce a high yield in the range of 71%
90% in both D- and L-forms of glyceric acid when compared with Acetobacter sp.
In 174 g/L pretreated glycerol with activated charcoal, Gluconobacter sp.
NBRC3259 could produce 49.5 and 28.2 g/L of glyceric acid (Carreira et al., 2011).
Additives, detergents, paper, paint, textile
Chemical industry
industry
Antioxidants, emulsifiers, thickening agent,
Food industry
preservatives, stabilizer
Pharmaceutical Laxatives, syrups, tanning agent, gastero
industry intestinal disorder
Livestock feed Poultry feed, pig diet, cow, and other animal
Glycerol
industry feed
Biotechnology Primary and secondary metabolites
industry
Personal care Toothpaste, cosmetics
industries
Other industries Cryoprotectant agent, thermoregulatory
agent, osmoregulatory agent
Figure 9.2 Application of glycerol in various industrial process.