Page 294 - Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
P. 294
262 Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
tops and leaves (trash) during the harvesting procedures. The energy obtained from
the recoverable dry leaf is equivalent to 10 tons of coal per hectare which is of one-
third of energy total energy available. Sugarcane mills possess significant contribu-
tion in the production of exportable energy from the cane trash with the reduced
release of carbon dioxide compared to conventional fossil fuel systems. The energy
produced from sugarcane is significantly higher than the energy obtained from the
coal. The cost of production also cheaper for sugarcane sources when compared to
crude oil/coal with carbon capture. Dry cane trash has the potential to replace the
natural energy deficit by 50%, as it generates high potential energy for cogeneration
process.
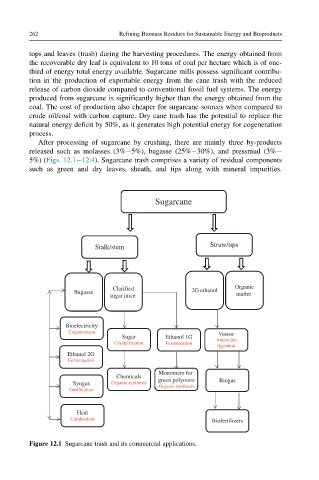
After processing of sugarcane by crushing, there are mainly three by-products
released such as molasses (3% 5%), bagasse (25% 30%), and pressmud (3%
5%) (Figs. 12.1 12.4). Sugarcane trash comprises a variety of residual components
such as green and dry leaves, sheath, and tips along with mineral impurities.
Sugarcane
Stalk/stem Straw/tips
Clarified 2G ethanol Organic
Bagasse matter
sugar juice
Bioelectricity
Cogeneration Vinasse
Sugar Ethanol 1G
Crystallization Fermentation Anaerobic
digestion
Ethanol 2G
Fermentation
Monomers for
Chemicals
Syngas Organic synthesis green polymers Biogas
Gasification Organic synthesis
Heat
Combustion Biofertilizers
Figure 12.1 Sugarcane trash and its commercial applications.