Page 335 - Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
P. 335
Pretreatment of agroindustry waste by ozonolysis for synthesis of biorefinery products 305
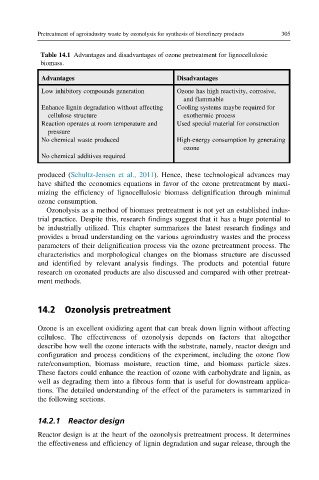
Table 14.1 Advantages and disadvantages of ozone pretreatment for lignocellulosic
biomass.
Advantages Disadvantages
Low inhibitory compounds generation Ozone has high reactivity, corrosive,
and flammable
Enhance lignin degradation without affecting Cooling systems maybe required for
cellulose structure exothermic process
Reaction operates at room temperature and Used special material for construction
pressure
No chemical waste produced High-energy consumption by generating
ozone
No chemical additives required
produced (Schultz-Jensen et al., 2011). Hence, these technological advances may
have shifted the economics equations in favor of the ozone pretreatment by maxi-
mizing the efficiency of lignocellulosic biomass delignification through minimal
ozone consumption.
Ozonolysis as a method of biomass pretreatment is not yet an established indus-
trial practice. Despite this, research findings suggest that it has a huge potential to
be industrially utilized. This chapter summarizes the latest research findings and
provides a broad understanding on the various agroindustry wastes and the process
parameters of their delignification process via the ozone pretreatment process. The
characteristics and morphological changes on the biomass structure are discussed
and identified by relevant analysis findings. The products and potential future
research on ozonated products are also discussed and compared with other pretreat-
ment methods.
14.2 Ozonolysis pretreatment
Ozone is an excellent oxidizing agent that can break down lignin without affecting
cellulose. The effectiveness of ozonolysis depends on factors that altogether
describe how well the ozone interacts with the substrate, namely, reactor design and
configuration and process conditions of the experiment, including the ozone flow
rate/consumption, biomass moisture, reaction time, and biomass particle sizes.
These factors could enhance the reaction of ozone with carbohydrate and lignin, as
well as degrading them into a fibrous form that is useful for downstream applica-
tions. The detailed understanding of the effect of the parameters is summarized in
the following sections.
14.2.1 Reactor design
Reactor design is at the heart of the ozonolysis pretreatment process. It determines
the effectiveness and efficiency of lignin degradation and sugar release, through the