Page 63 - Reliability and Maintainability of In service Pipelines
P. 63
52 Reliability and Maintainability of In-Service Pipelines
1% Corrosion
4.90% 8.90%
Construction and
assembly
Mechanical damage
44.10%
14.70%
Joints
8.80%
Natural disasters
17.60% Noncompliance with
standards
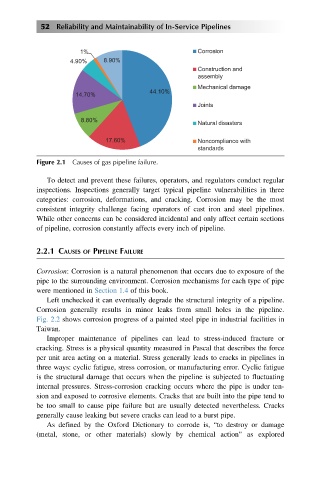
Figure 2.1 Causes of gas pipeline failure.
To detect and prevent these failures, operators, and regulators conduct regular
inspections. Inspections generally target typical pipeline vulnerabilities in three
categories: corrosion, deformations, and cracking. Corrosion may be the most
consistent integrity challenge facing operators of cast iron and steel pipelines.
While other concerns can be considered incidental and only affect certain sections
of pipeline, corrosion constantly affects every inch of pipeline.
2.2.1 CAUSES OF PIPELINE FAILURE
Corrosion: Corrosion is a natural phenomenon that occurs due to exposure of the
pipe to the surrounding environment. Corrosion mechanisms for each type of pipe
were mentioned in Section 1.4 of this book.
Left unchecked it can eventually degrade the structural integrity of a pipeline.
Corrosion generally results in minor leaks from small holes in the pipeline.
Fig. 2.2 shows corrosion progress of a painted steel pipe in industrial facilities in
Taiwan.
Improper maintenance of pipelines can lead to stress-induced fracture or
cracking. Stress is a physical quantity measured in Pascal that describes the force
per unit area acting on a material. Stress generally leads to cracks in pipelines in
three ways: cyclic fatigue, stress corrosion, or manufacturing error. Cyclic fatigue
is the structural damage that occurs when the pipeline is subjected to fluctuating
internal pressures. Stress-corrosion cracking occurs where the pipe is under ten-
sion and exposed to corrosive elements. Cracks that are built into the pipe tend to
be too small to cause pipe failure but are usually detected nevertheless. Cracks
generally cause leaking but severe cracks can lead to a burst pipe.
As defined by the Oxford Dictionary to corrode is, “to destroy or damage
(metal, stone, or other materials) slowly by chemical action” as explored