Page 20 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 20
Renewable Energy Systems: Technology Overview and Perspectives 7
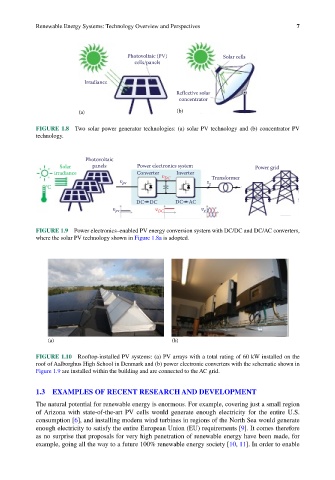
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar cells
cells/panels
Irradiance
Reflective solar
concentrator
(a) (b)
FIGURE 1.8 Two solar power generator technologies: (a) solar PV technology and (b) concentrator PV
technology.
Photovoltaic
Solar panels Power electronics system Power grid
irradiance Converter υ Inverter
υ pv DC υ g Transformer
°C
DC DC DC AC
υ pv υ DC υ g
FIGURE 1.9 Power electronics–enabled PV energy conversion system with DC/DC and DC/AC converters,
where the solar PV technology shown in Figure 1.8a is adopted.
(a) (b)
FIGURE 1.10 Rooftop-installed PV systems: (a) PV arrays with a total rating of 60 kW installed on the
roof of Aalborghus High School in Denmark and (b) power electronic converters with the schematic shown in
Figure 1.9 are installed within the building and are connected to the AC grid.
1.3 EXAMPLES OF RECENT RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
The natural potential for renewable energy is enormous. For example, covering just a small region
of Arizona with state-of-the-art PV cells would generate enough electricity for the entire U.S.
consumption [6], and installing modern wind turbines in regions of the North Sea would generate
enough electricity to satisfy the entire European Union (EU) requirements [9]. It comes therefore
as no surprise that proposals for very high penetration of renewable energy have been made, for
example, going all the way to a future 100% renewable energy society [10, 11]. In order to enable