Page 24 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 24
Renewable Energy Systems: Technology Overview and Perspectives 11
and survivability during storms are major challenges that drive up the investment, operation and
maintenance efforts, and ultimately the final cost of energy for such system. Although systems such
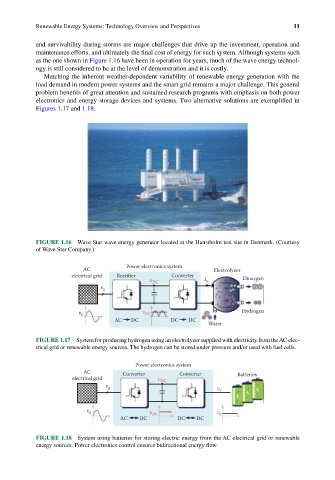
as the one shown in Figure 1.16 have been in operation for years, much of the wave energy technol-
ogy is still considered to be at the level of demonstration and it is costly.
Matching the inherent weather-dependent variability of renewable energy generation with the
load demand in modern power systems and the smart grid remains a major challenge. This general
problem benefits of great attention and sustained research programs with emphasis on both power
electronics and energy storage devices and systems. Two alternative solutions are exemplified in
Figures 1.17 and 1.18.
FIGURE 1.16 Wave Star wave energy generator located at the Hanstholm test site in Denmark. (Courtesy
of Wave Star Company.)
Power electronics system
AC Electrolyzer
electrical grid Rectifier Converter
υ DC i o + Dioxygen
υ g H O H OO OO
O
H H O O
H
O H H H H
O H H H H HH
H H H
υ g υ DC O – Hydrogen
AC DC DC DC H H
Water
FIGURE 1.17 System for producing hydrogen using an electrolyzer supplied with electricity from the AC elec-
trical grid or renewable energy sources. The hydrogen can be stored under pressure and/or used with fuel cells.
Power electronics system
AC Converter Converter Batteries
electrical grid υ DC
υ g υ o
υ g υ DC υ o
AC DC DC DC
FIGURE 1.18 System using batteries for storing electric energy from the AC electrical grid or renewable
energy sources. Power electronics control ensures bidirectional energy flow.