Page 275 - Reservoir Formation Damage
P. 275
Two-Phase Formation Damage by Fines Migration 255
0.1:
0.01
0.5 1 1.5
Pore Volume of Injected Fluid
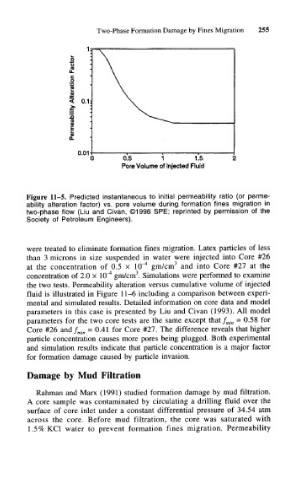
Figure 11-5. Predicted instantaneous to initial permeability ratio (or perme-
ability alteration factor) vs. pore volume during formation fines migration in
two-phase flow (Liu and Civan, ©1996 SPE; reprinted by permission of the
Society of Petroleum Engineers).
were treated to eliminate formation fines migration. Latex particles of less
than 3 microns in size suspended in water were injected into Core #26
at the concentration of 0.5 x 10~ 4 gm/cm 3 and into Core #27 at the
4
3
concentration of 2.0 x 10" gm/cm . Simulations were performed to examine
the two tests. Permeability alteration versus cumulative volume of injected
fluid is illustrated in Figure 11-6 including a comparison between experi-
mental and simulated results. Detailed information on core data and model
parameters in this case is presented by Liu and Civan (1993). All model
parameters for the two core tests are the same except thatf min = 0.58 for
Core #26 and/„,,-„ = 0.41 for Core #27. The difference reveals that higher
particle concentration causes more pores being plugged. Both experimental
and simulation results indicate that particle concentration is a major factor
for formation damage caused by particle invasion.
Damage by Mud Filtration
Rahman and Marx (1991) studied formation damage by mud filtration.
A core sample was contaminated by circulating a drilling fluid over the
surface of core inlet under a constant differential pressure of 34.54 atm
across the core. Before mud filtration, the core was saturated with
1.5% KC1 water to prevent formation fines migration. Permeability