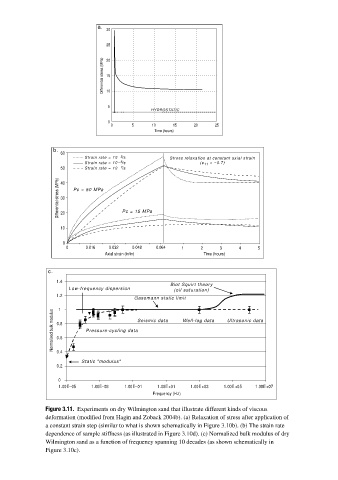
Page 93 - Reservoir Geomechanics
P. 93
a.
30
25
Differential stress (MPa) 20
15
10
5
HYDROSTATIC
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
Time (hours)
b.
60
Strain rate = 10 −5 /s Stress relaxation at constant axial strain
Strain rate = 10 −6 /s (e 11 = ~0.7)
50 Strain rate = 10 −7 /s
Differential stress (MPa) 30 Pc = 50 MPa Pc = 15 MPa
40
20
10
0
0 0.016 0.032 0.048 0.064 1 2 3 4 5
Axial strain (in/in) Time (hours)
c.
1.4
Biot Squirt theory
Low-frequency dispersion (oil saturation)
1.2
Gassmann static limit
1
Normalized bulk modulus 0.8 Pressure-cycling data Seismic data Well-log data Ultrasonic data
0.6
0.4
Static "modulus"
0.2
0
1.00E−05 1.00E−03 1.00E−01 1.00E+01 1.00E+03 1.00E+05 1.00E+07
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 3.11. Experiments on dry Wilmington sand that illustrate different kinds of viscous
deformation (modified from Hagin and Zoback 2004b). (a) Relaxation of stress after application of
a constant strain step (similar to what is shown schematically in Figure 3.10b). (b) The strain rate
dependence of sample stiffness (as illustrated in Figure 3.10d). (c) Normalized bulk modulus of dry
Wilmington sand as a function of frequency spanning 10 decades (as shown schematically in
Figure 3.10c).