Page 434 - Robot Builder's Bonanza
P. 434
SWITCHES 403
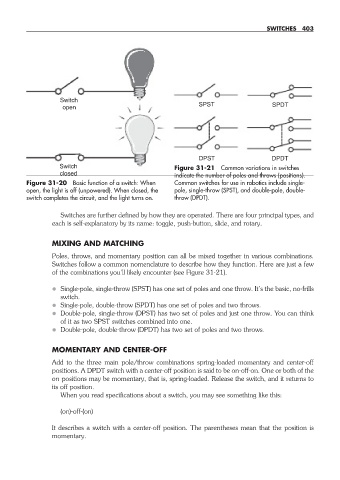
Switch
open SPST SPDT
DPST DPDT
Switch Figure 31- 21 Common variations in switches
closed indicate the number of poles and throws (positions).
Figure 31- 20 Basic function of a switch: When Common switches for use in robotics include single-
open, the light is off (unpowered). When closed, the pole, single- throw (SPST), and double- pole, double-
switch completes the circuit, and the light turns on. throw (DPDT).
Switches are further defined by how they are operated. There are four principal types, and
each is self- explanatory by its name: toggle, push- button, slide, and rotary.
MIXING AND MATCHING
Poles, throws, and momentary position can all be mixed together in various combinations.
Switches follow a common nomenclature to describe how they function. Here are just a few
of the combinations you’ll likely encounter (see Figure 31- 21).
• Single- pole, single- throw (SPST) has one set of poles and one throw. It’s the basic, no- frills
switch.
• Single- pole, double- throw (SPDT) has one set of poles and two throws.
• Double- pole, single- throw (DPST) has two set of poles and just one throw. You can think
of it as two SPST switches combined into one.
• Double- pole, double- throw (DPDT) has two set of poles and two throws.
MOMENTARY AND CENTER- OFF
Add to the three main pole/throw combinations spring- loaded momentary and center- off
positions. A DPDT switch with a center- off position is said to be on- off- on. One or both of the
on positions may be momentary, that is, spring- loaded. Release the switch, and it returns to
its off position.
When you read specifications about a switch, you may see something like this:
(on)-off- (on)
It describes a switch with a center- off position. The parentheses mean that the position is
momentary.
31-chapter-31.indd 403 4/21/11 11:56 AM