Page 118 -
P. 118
2.11 Linear Controller Design 99
This can be achieved using the structure of Figure 2.11.1 using the gain
found in Example 2.11.1
The double integrator system being both controllable and observable, also’
lends itself to the most general controller design technique for linear systems,
namely the two-degree -f freedom (2-DOF) design. This allows the
controlled closed-loop system to match any desired model as descried in
[Kailath 1980]. This approach goes beyond the pole or eigenvalue placement
designs, as one can now move both poles and zeros, a goal not achievable
with the observer-controller compensators. This design is illustrated in the
following example.
EXAMPLE 2.11–4: Two DOF Design
Consider again the double integrator system, and assume the desired closed-
loop transfer function is given by
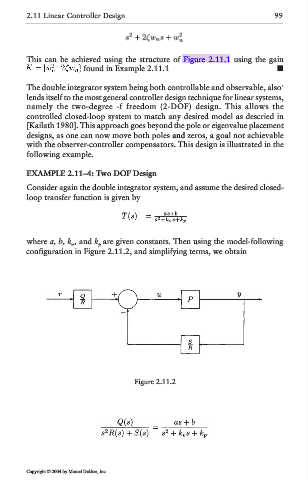
where a, b, k v, and k p are given constants. Then using the model-following
configuration in Figure 2.11.2, and simplifying terms, we obtain
Figure 2.11.2
Copyright © 2004 by Marcel Dekker, Inc.