Page 89 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 89
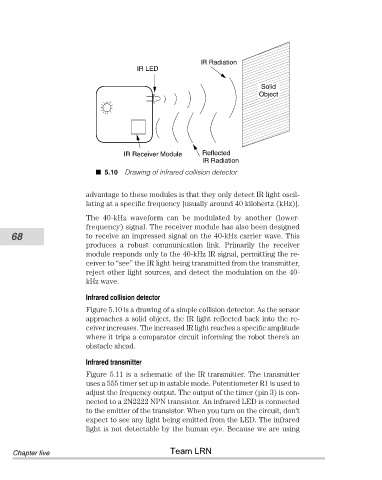
IR LED IR Radiation
Solid
Object
IR Receiver Module Reflected
IR Radiation
5.10 Drawing of infrared collision detector
advantage to these modules is that they only detect IR light oscil-
lating at a specific frequency [usually around 40 kilohertz (kHz)].
The 40-kHz waveform can be modulated by another (lower-
frequency) signal. The receiver module has also been designed
68 to receive an impressed signal on the 40-kHz carrier wave. This
produces a robust communication link. Primarily the receiver
module responds only to the 40-kHz IR signal, permitting the re-
ceiver to “see” the IR light being transmitted from the transmitter,
reject other light sources, and detect the modulation on the 40-
kHz wave.
Infrared collision detector
Figure 5.10 is a drawing of a simple collision detector. As the sensor
approaches a solid object, the IR light reflected back into the re-
ceiver increases. The increased IR light reaches a specific amplitude
where it trips a comparator circuit informing the robot there’s an
obstacle ahead.
Infrared transmitter
Figure 5.11 is a schematic of the IR transmitter. The transmitter
uses a 555 timer set up in astable mode. Potentiometer R1 is used to
adjust the frequency output. The output of the timer (pin 3) is con-
nected to a 2N2222 NPN transistor. An infrared LED is connected
to the emitter of the transistor. When you turn on the circuit, don’t
expect to see any light being emitted from the LED. The infrared
light is not detectable by the human eye. Because we are using
Team LRN
Chapter five