Page 325 - Rock Mechanics For Underground Mining
P. 325
CHARACTERISATION OF SEISMIC EVENTS
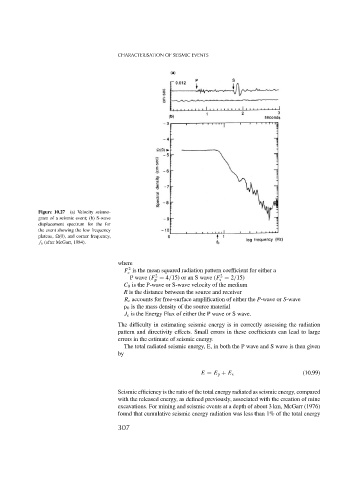
Figure 10.27 (a) Velocity seismo-
gram of a seismic event; (b) S-wave
displacement spectrum for the for
the event showing the low frequency
plateau, (0), and corner frequency,
f o (after McGarr, 1984).
where
2
F is the mean squared radiation pattern coefficient for either a
c
2
2
Pwave(F = 4/15) or an S wave (F = 2/15)
p s
C 0 is the P-wave or S-wave velocity of the medium
R is the distance between the source and receiver
R c accounts for free-surface amplification of either the P-wave or S-wave
0 is the mass density of the source material
J c is the Energy Flux of either the P wave or S wave.
The difficulty in estimating seismic energy is in correctly assessing the radiation
pattern and directivity effects. Small errors in these coefficients can lead to large
errors in the estimate of seismic energy.
The total radiated seismic energy, E, in both the P wave and S wave is then given
by
(10.99)
E = E p + E s
Seismic efficiency is the ratio of the total energy radiated as seismic energy, compared
with the released energy, as defined previously, associated with the creation of mine
excavations. For mining and seismic events at a depth of about 3 km, McGarr (1976)
found that cumulative seismic energy radiation was less than 1% of the total energy
307