Page 89 - Root Cause Failure Analysis
P. 89
80 Root Cause Failure Analysis
the total vertical lift or elevation change, friction losses in the piping, and flow restric-
tions caused by the process. Other variables affecting performance include the pump's
hydraulic curve and brake horsepower.
Suction Conditions
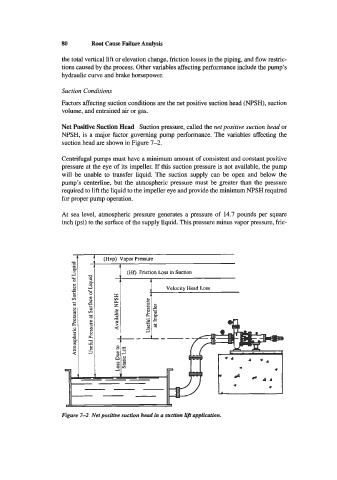
Factors affecting suction conditions are the net positive suction head (NF'SH), suction
volume, and entrained air or gas.
Net Positive Suction Head Suction pressure, called the net positive suction head or
NPSH, is a major factor governing pump performance. The variables affecting the
suction head are shown in Figure 7-2.
Centrifugal pumps must have a minimum amount of consistent and constant positive
pressure at the eye of its impeller. If this suction pressure is not available, the pump
will be unable to transfer liquid. The suction supply can be open and below the
pump's centerline, but the atmospheric pressure must be greater than the pressure
required to lift the liquid to the impeller eye and provide the minimum NF'SH required
for proper pump operation.
At sea level, atmospheric pressure generates a pressure of 14.7 pounds per square
inch (psi) to the surface of the supply liquid. This pressure minus vapor pressure, fric-
Figure 7-2 Net positive suction head in a suction lifi application.