Page 136 - Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
P. 136
Risk Analysis Techniques 115
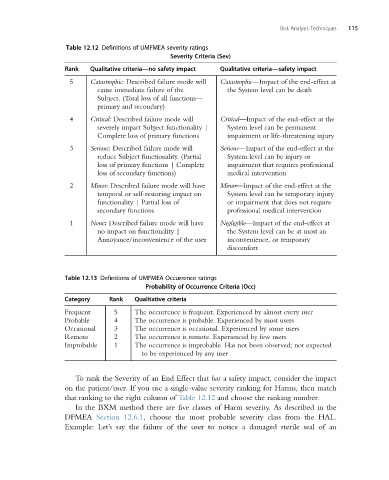
Table 12.12 Definitions of UMFMEA severity ratings
Severity Criteria (Sev)
Rank Qualitative criteria—no safety impact Qualitative criteria—safety impact
5 Catastrophic: Described failure mode will Catastrophic—Impact of the end-effect at
cause immediate failure of the the System level can be death
Subject. (Total loss of all functions—
primary and secondary)
4 Critical: Described failure mode will Critical—Impact of the end-effect at the
severely impact Subject functionality | System level can be permanent
Complete loss of primary functions impairment or life-threatening injury
3 Serious: Described failure mode will Serious—Impact of the end-effect at the
reduce Subject functionality. (Partial System level can be injury or
loss of primary functions | Complete impairment that requires professional
loss of secondary functions) medical intervention
2 Minor: Described failure mode will have Minor—Impact of the end-effect at the
temporal or self-restoring impact on System level can be temporary injury
functionality | Partial loss of or impairment that does not require
secondary functions professional medical intervention
1 None: Described failure mode will have Negligible—Impact of the end-effect at
no impact on functionality | the System level can be at most an
Annoyance/inconvenience of the user inconvenience, or temporary
discomfort
Table 12.13 Definitions of UMFMEA Occurrence ratings
Probability of Occurrence Criteria (Occ)
Category Rank Qualitative criteria
Frequent 5 The occurrence is frequent. Experienced by almost every user
Probable 4 The occurrence is probable. Experienced by most users
Occasional 3 The occurrence is occasional. Experienced by some users
Remote 2 The occurrence is remote. Experienced by few users
Improbable 1 The occurrence is improbable. Has not been observed; not expected
to be experienced by any user
To rank the Severity of an End Effect that has a safety impact, consider the impact
on the patient/user. If you use a single-value severity ranking for Harms, then match
that ranking to the right column of Table 12.12 and choose the ranking number.
In the BXM method there are five classes of Harm severity. As described in the
DFMEA Section 12.6.1, choose the most probable severity class from the HAL.
Example: Let’s say the failure of the user to notice a damaged sterile seal of an