Page 245 - Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
P. 245
224 Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
top three classes of Catastrophic, Critical, and Serious. Also sum the residual risk for
the bottom two severity classes. If the top three classes are more than twice the bot-
tom two classes, then declare the design output as EDO. Of course, this is a suggested
strategy and you can adapt it to suit your Quality Management System. The main
point is to have a rational and documented strategy.
31.2 LIFECYCLE RELEVANCE OF RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk management is an activity that adds value to the product development lifecycle.
Companies who view risk management as a necessary evil, and a box that needs to be
checked in order to get their product approved, miss out on the value that they could
derive from risk management.
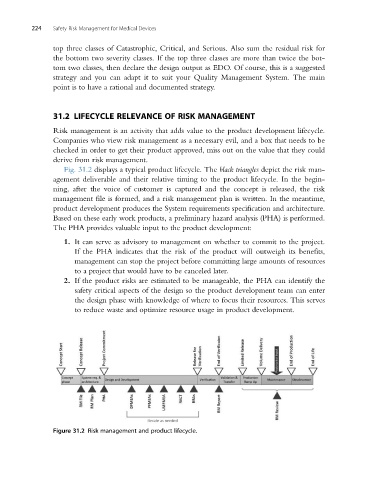
Fig. 31.2 displays a typical product lifecycle. The black triangles depict the risk man-
agement deliverable and their relative timing to the product lifecycle. In the begin-
ning, after the voice of customer is captured and the concept is released, the risk
management file is formed, and a risk management plan is written. In the meantime,
product development produces the System requirements specification and architecture.
Based on these early work products, a preliminary hazard analysis (PHA) is performed.
The PHA provides valuable input to the product development:
1. It can serve as advisory to management on whether to commit to the project.
If the PHA indicates that the risk of the product will outweigh its benefits,
management can stop the project before committing large amounts of resources
to a project that would have to be canceled later.
2. If the product risks are estimated to be manageable, the PHA can identify the
safety critical aspects of the design so the product development team can enter
the design phase with knowledge of where to focus their resources. This serves
to reduce waste and optimize resource usage in product development.
Figure 31.2 Risk management and product lifecycle.