Page 31 - Satellite Communications, Fourth Edition
P. 31
Overview of Satellite Systems 11
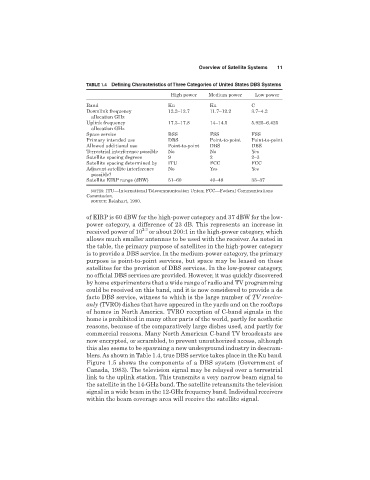
TABLE 1.4 Defining Characteristics of Three Categories of United States DBS Systems
High power Medium power Low power
Band Ku Ku C
Downlink frequency 12.2–12.7 11.7–12.2 3.7–4.2
allocation GHz
Uplink frequency 17.3–17.8 14–14.5 5.925–6.425
allocation GHz
Space service BSS FSS FSS
Primary intended use DBS Point-to-point Point-to-point
Allowed additional use Point-to-point DBS DBS
Terrestrial interference possible No No Yes
Satellite spacing degrees 9 2 2–3
Satellite spacing determined by ITU FCC FCC
Adjacent satellite interference No Yes Yes
possible?
Satellite EIRP range (dBW) 51–60 40–48 33–37
NOTES: ITU—International Telecommunication Union; FCC—Federal Communications
Commission.
SOURCE: Reinhart, 1990.
of EIRP is 60 dBW for the high-power category and 37 dBW for the low-
power category, a difference of 23 dB. This represents an increase in
received power of 10 2.3 or about 200:1 in the high-power category, which
allows much smaller antennas to be used with the receiver. As noted in
the table, the primary purpose of satellites in the high-power category
is to provide a DBS service. In the medium-power category, the primary
purpose is point-to-point services, but space may be leased on these
satellites for the provision of DBS services. In the low-power category,
no official DBS services are provided. However, it was quickly discovered
by home experimenters that a wide range of radio and TV programming
could be received on this band, and it is now considered to provide a de
facto DBS service, witness to which is the large number of TV receive-
only (TVRO) dishes that have appeared in the yards and on the rooftops
of homes in North America. TVRO reception of C-band signals in the
home is prohibited in many other parts of the world, partly for aesthetic
reasons, because of the comparatively large dishes used, and partly for
commercial reasons. Many North American C-band TV broadcasts are
now encrypted, or scrambled, to prevent unauthorized access, although
this also seems to be spawning a new underground industry in descram-
blers. As shown in Table 1.4, true DBS service takes place in the Ku band.
Figure 1.5 shows the components of a DBS system (Government of
Canada, 1983). The television signal may be relayed over a terrestrial
link to the uplink station. This transmits a very narrow beam signal to
the satellite in the 14-GHz band. The satellite retransmits the television
signal in a wide beam in the 12-GHz frequency band. Individual receivers
within the beam coverage area will receive the satellite signal.