Page 35 - Satellite Communications, Fourth Edition
P. 35
Overview of Satellite Systems 15
TABLE 1.6 Ka-Band Orbital Assignment Plan (FCC December 19, 1997) (Continued )
Location Company
111°E.L. Hughes Communications Galaxy, Inc.
114.5°E.L. GE American Communications, Inc.
124.5°E.L PanAmSat Corporation
126.5°E.L. Orion Network Systems, Inc.
130°E.L. Lockheed Martin Corporation
149°E.L. Hughes Communications Galaxy, Inc.
164°E.L. Hughes Communications Galaxy, Inc.
173°E.L. PanAmSat Corporation
175.25°E.L. Lockheed Martin Corporation
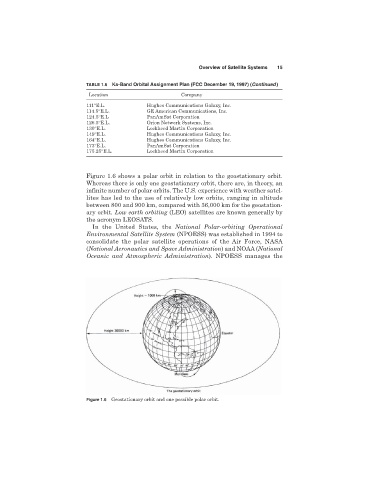
Figure 1.6 shows a polar orbit in relation to the geostationary orbit.
Whereas there is only one geostationary orbit, there are, in theory, an
infinite number of polar orbits. The U.S. experience with weather satel-
lites has led to the use of relatively low orbits, ranging in altitude
between 800 and 900 km, compared with 36,000 km for the geostation-
ary orbit. Low earth orbiting (LEO) satellites are known generally by
the acronym LEOSATS.
In the United States, the National Polar-orbiting Operational
Environmental Satellite System (NPOESS) was established in 1994 to
consolidate the polar satellite operations of the Air Force, NASA
(National Aeronautics and Space Administration) and NOAA (National
Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). NPOESS manages the
Figure 1.6 Geostationary orbit and one possible polar orbit.