Page 312 - Satellite Communications, Fourth Edition
P. 312
292 Chapter Ten
the bit rate would be 56 kb/s. Various data reduction schemes are in use
which give much greater reductions, and some of these can achieve bit
rates as low as 2400 b/s (Hassanein et al., 1989 and 1992).
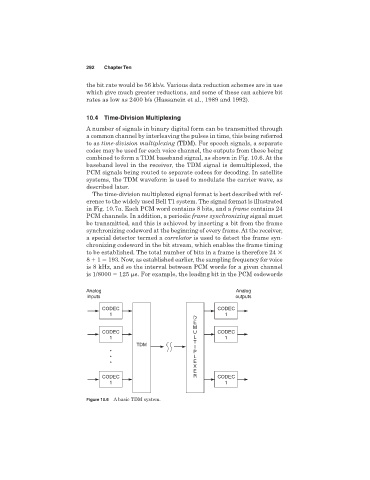
10.4 Time-Division Multiplexing
A number of signals in binary digital form can be transmitted through
a common channel by interleaving the pulses in time, this being referred
to as time-division multiplexing (TDM). For speech signals, a separate
codec may be used for each voice channel, the outputs from these being
combined to form a TDM baseband signal, as shown in Fig. 10.6. At the
baseband level in the receiver, the TDM signal is demultiplexed, the
PCM signals being routed to separate codecs for decoding. In satellite
systems, the TDM waveform is used to modulate the carrier wave, as
described later.
The time-division multiplexed signal format is best described with ref-
erence to the widely used Bell T1 system. The signal format is illustrated
in Fig. 10.7a. Each PCM word contains 8 bits, and a frame contains 24
PCM channels. In addition, a periodic frame synchronizing signal must
be transmitted, and this is achieved by inserting a bit from the frame
synchronizing codeword at the beginning of every frame. At the receiver,
a special detector termed a correlator is used to detect the frame syn-
chronizing codeword in the bit stream, which enables the frame timing
to be established. The total number of bits in a frame is therefore 24
8 1 193. Now, as established earlier, the sampling frequency for voice
is 8 kHz, and so the interval between PCM words for a given channel
is 1/8000 125 s. For example, the leading bit in the PCM codewords
Analog Analog
inputs outputs
CODEC CODEC
1 1
D
E
M
CODEC U CODEC
1 L 1
T
TDM
I
• P
• L
• E
X
E
CODEC R CODEC
1 1
Figure 10.6 A basic TDM system.