Page 69 - Satellite Communications, Fourth Edition
P. 69
Orbits and Launching Methods 49
Denoting the reference time as JD , the Julian century by JC, and
ref
the time in question by JD, then the interval in Julian centuries from
the reference time to the time in question is given by
JD JD ref
T (2.20)
JC
This is illustrated in the following example.
Example 2.11 Find the time in Julian centuries from the reference time January
0.5, 1900 to 13 h UT on 18 December 2000.
Solution JD ref 2415020 days; JC 36525 days. From Example 2.10: JD
2451897.0417 days. Equation (2.20) gives
2451897.0417 2415020
T
36525
1.00963838
Note that the time units are days and T is dimensionless.
2.9.4 Sidereal time
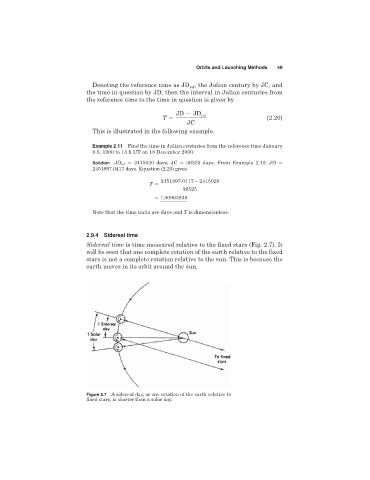
Sidereal time is time measured relative to the fixed stars (Fig. 2.7). It
will be seen that one complete rotation of the earth relative to the fixed
stars is not a complete rotation relative to the sun. This is because the
earth moves in its orbit around the sun.
Figure 2.7 A sidereal day, or one rotation of the earth relative to
fixed stars, is shorter than a solar day.