Page 203 - Schaum's Outline of Differential Equations
P. 203
186 NUMERICAL METHODS FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS [CHAP. 19
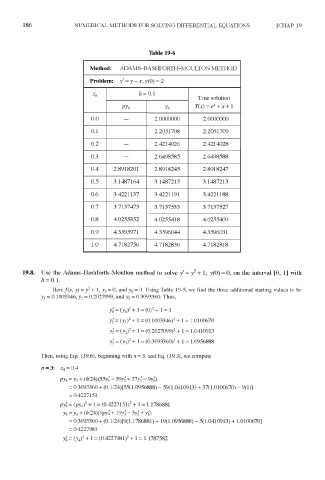
Table 19-6
Method: ADAMS-BASHFORTH-MOULTON METHOD
Problem: y' = y-x; y(0) = 2
h = 0.1
x n
True solution
py n y n Y(x) = (f + x + 1
0.0 — 2.0000000 2.0000000
0.1 — 2.2051708 2.2051709
0.2 — 2.4214026 2.4214028
0.3 — 2.6498585 2.6498588
0.4 2.8918201 2.8918245 2.8918247
0.5 3.1487164 3.1487213 3.1487213
0.6 3.4221137 3.4221191 3.4221188
0.7 3.7137473 3.7137533 3.7137527
0.8 4.0255352 4.0255418 4.0255409
0.9 4.3595971 4.3596044 4.3596031
1.0 4.7182756 4.7182836 4.7182818
1
19.8. Use the Adams-Bashforth-Moulton method to solve y' = y + 1; y(0) = 0, on the interval [0, 1] with
h = 0.l.
2
Here f(x, y) = y + 1, x 0 = 0, and y 0 = 0. Using Table 19-5, we find the three additional starting values to be
= 0.3093360. Thus,
y 1 = 0.1003346, y 2 = 0.2027099, and y 3
Then, using Eqs. (19.6), beginning with n = 3, and Eq. (19.3), we compute