Page 448 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 448
CHAP. 35] THE SOLID STATE 433
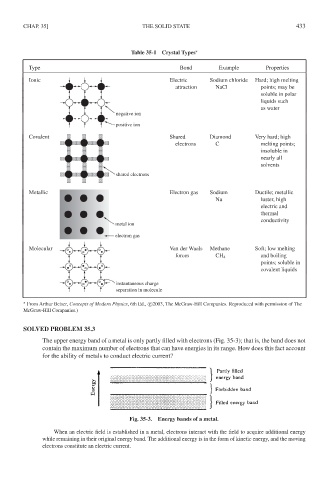
Table 35-1 Crystal Types ∗
Type Bond Example Properties
Ionic Electric Sodium chloride Hard; high melting
attraction NaCl points; may be
soluble in polar
liquids such
as water
negative ion
positive ion
Covalent Shared Diamond Very hard; high
electrons C melting points;
insoluble in
nearly all
solvents
shared electrons
Metallic Electron gas Sodium Ductile; metallic
Na luster, high
electric and
thermal
conductivity
metal ion
electron gas
Molecular Van der Waals Methane Soft; low melting
forces CH 4 and boiling
points; soluble in
covalent liquids
instantaneous charge
separation in molecule
∗ From Arthur Beiser, Conceptsof Modern Physics, 6th Ed., c 2003, The McGraw-Hill Companies. Reproduced with permission of The
McGraw-Hill Companies.)
SOLVED PROBLEM 35.3
The upper energy band of a metal is only partly filled with electrons (Fig. 35-3); that is, the band does not
contain the maximum number of electrons that can have energies in its range. How does this fact account
for the ability of metals to conduct electric current?
Fig. 35-3. Energy bands of a metal.
When an electric field is established in a metal, electrons interact with the field to acquire additional energy
while remaining in their original energy band. The additional energy is in the form of kinetic energy, and the moving
electrons constitute an electric current.