Page 42 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 42
CIRCUIT LAWS
CHAP. 3]
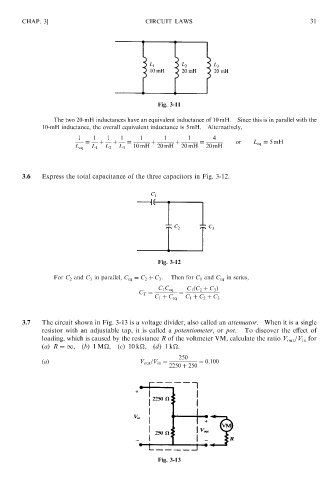
Fig. 3-11 31
The two 20-mH inductances have an equivalent inductance of 10 mH. Since this is in parallel with the
10-mH inductance, the overall equivalent inductance is 5 mH. Alternatively,
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4
¼ þ þ ¼ þ þ ¼ or L eq ¼ 5mH
L eq L 1 L 2 L 3 10 mH 20 mH 20 mH 20 mH
3.6 Express the total capacitance of the three capacitors in Fig. 3-12.
Fig. 3-12
For C 2 and C 3 in parallel, C eq ¼ C 2 þ C 3 . Then for C 1 and C eq in series,
C 1 C eq C 1 ðC 2 þ C 3 Þ
C T ¼ ¼
C 1 þ C eq C 1 þ C 2 þ C 3
3.7 The circuit shown in Fig. 3-13 is a voltage divider, also called an attenuator. When it is a single
resistor with an adjustable tap, it is called a potentiometer,or pot. To discover the effect of
loading, which is caused by the resistance R of the voltmeter VM, calculate the ratio V out =V in for
(a) R ¼1,(b)1 M
, (c)10 k
,(d)1 k
.
250
ðaÞ V out =V in ¼ ¼ 0:100
2250 þ 250
Fig. 3-13