Page 43 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 43
CIRCUIT LAWS
32
(b) The resistance R in parallel with the 250-
resistor has an equivalent resistance [CHAP. 3
6
250ð10 Þ 249:9
R eq ¼ ¼ 249:9
and V out =V in ¼ ¼ 0:100
250 þ 10 6 2250 þ 249:9
ð250Þð10 000Þ
ðcÞ R eq ¼ ¼ 243:9
and V out =V in ¼ 0:098
250 þ 10 000
ð250Þð1000Þ
ðdÞ R eq ¼ ¼ 200:0
and V out =V in ¼ 0:082
250 þ 1000
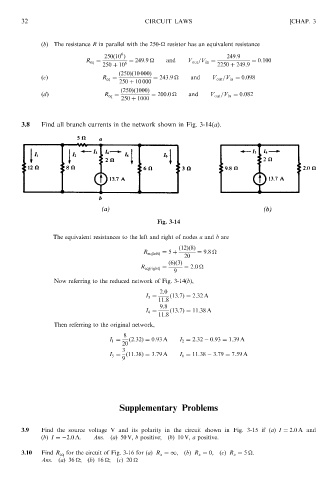
3.8 Find all branch currents in the network shown in Fig. 3-14(a).
Fig. 3-14
The equivalent resistances to the left and right of nodes a and b are
ð12Þð8Þ
R eqðleftÞ ¼ 5 þ ¼ 9:8
20
ð6Þð3Þ
R eqðrightÞ ¼ ¼ 2:0
9
Now referring to the reduced network of Fig. 3-14(b),
2:0
I 3 ¼ ð13:7Þ¼ 2:32 A
11:8
9:8
I 4 ¼ ð13:7Þ¼ 11:38 A
11:8
Then referring to the original network,
8
I 1 ¼ ð2:32Þ¼ 0:93 A I 2 ¼ 2:32 0:93 ¼ 1:39 A
20
3
I 5 ¼ ð11:38Þ¼ 3:79 A I 6 ¼ 11:38 3:79 ¼ 7:59 A
9
Supplementary Problems
3.9 Find the source voltage V and its polarity in the circuit shown in Fig. 3-15 if (a) I ¼ 2:0 A and
(b) I ¼ 2:0A. Ans. (a)50 V, b positive; (b)10 V, a positive.
3.10 Find R eq for the circuit of Fig. 3-16 for (a) R x ¼1, (b) R x ¼ 0, (c) R x ¼ 5
.
Ans.(a)36
; (b)16
; (c)20