Page 72 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 72
ANALYSIS METHODS
CHAP. 4]
Fig. 4-47 61
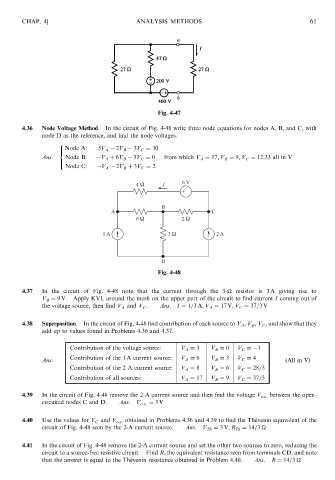
4.36 Node Voltage Method. In the circuit of Fig. 4-48 write three node equations for nodes A, B, and C, with
node D as the reference, and find the node voltages.
8
> Node A: 5V A 2V B 3V C ¼ 30
<
Ans: Node B: V A þ 6V B 3V C ¼ 0 from which V A ¼ 17; V B ¼ 9; V C ¼ 12:33 all in V
>
:
Node C: V A 2V B þ 3V C ¼ 2
Fig. 4-48
4.37 In the circuit of Fig. 4-48 note that the current through the 3-
resistor is 3 A giving rise to
V B ¼ 9 V. Apply KVL around the mesh on the upper part of the circuit to find current I coming out of
the voltage source, then find V A and V C . Ans: I ¼ 1=3A; V A ¼ 17 V; V C ¼ 37=3V
4.38 Superposition. In the circuit of Fig. 4-48 find contribution of each source to V A , V B , V C , and show that they
add up to values found in Problems 4.36 and 4.37.
Contribution of the voltage source: V A ¼ 3 V B ¼ 0 V C ¼ 1
Contribution of the 1 A current source: V A ¼ 6 V B ¼ 3 V C ¼ 4
Ans. (All in V)
Contribution of the 2 A current source: V A ¼ 8 V B ¼ 6 V C ¼ 28=3
Contribution of all sources: V A ¼ 17 V B ¼ 9 V C ¼ 37=3
4.39 In the circuit of Fig. 4-48 remove the 2-A current source and then find the voltage V o:c: between the open-
circuited nodes C and D. Ans: V o:c: ¼ 3V
4.40 Use the values for V C and V o:c: obtained in Problems 4.36 and 4.39 to find the The ´ venin equivalent of the
circuit of Fig. 4-48 seen by the 2-A current source. Ans: V Th ¼ 3V; R Th ¼ 14=3
4.41 In the circuit of Fig. 4-48 remove the 2-A current source and set the other two sources to zero, reducing the
circuit to a source-free resistive circuit. Find R, the equivalent resistance seen from terminals CD, and note
that the answer is equal to the The ´ venin resistance obtained in Problem 4.40. Ans: R ¼ 14=3