Page 74 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 74
63
ANALYSIS METHODS
CHAP. 4]
4.46 Loop Current Method. In the circuit of Fig. 4-51 write two loop equations using I 1 and I 2 as loop currents,
then find the currents and node voltages.
Loop 1: 4I 1 I 2 ¼ 2 I 1 ¼ 1A; I 2 ¼ 2A
Ans: from which,
Loop 2: I 1 þ 2I 2 ¼ 3 V A ¼ 9V; V B ¼ 5V; V C ¼ 2V
4.47 Superposition. In the circuit of Fig. 4-51 find the contribution of each source to V A , V B , V C , and show that
they add up to values found in Problem 4.45.
From the current source: V A ¼ 7:429 V B ¼ 3:143 V C ¼ 1:429
Ans. From the voltage source: V A ¼ 1:571 V B ¼ 1:857 V C ¼ 0:571 (all in V)
From both sources: V A ¼ 9 V B ¼ 5 V C ¼ 2
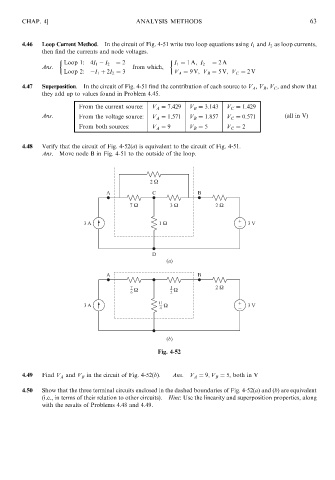
4.48 Verify that the circuit of Fig. 4-52(a) is equivalent to the circuit of Fig. 4-51.
Ans. Move node B in Fig. 4-51 to the outside of the loop.
Fig. 4-52
4.49 Find V A and V B in the circuit of Fig. 4-52(b). Ans: V A ¼ 9; V B ¼ 5, both in V
4.50 Show that the three terminal circuits enclosed in the dashed boundaries of Fig. 4-52(a) and (b) are equivalent
(i.e., in terms of their relation to other circuits). Hint: Use the linearity and superposition properties, along
with the results of Problems 4.48 and 4.49.