Page 22 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Signals and Systems
P. 22
CHAP. 11 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS 11
As illustrated in Fig. 1-8, if a > 0, then x(f ) is a growing exponential; and if a < 0, then
x(t) is a decaying exponential.
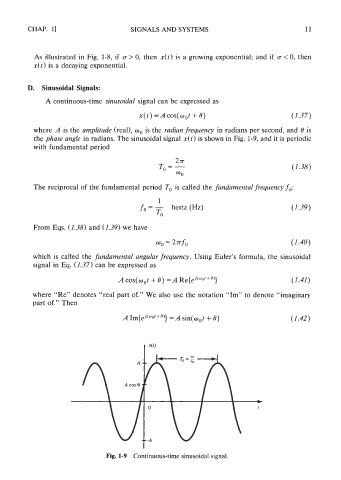
D. Sinusoidal Signals:
A continuous-time sinusoidal signal can be expressed as
where A is the amplitude (real), w, is the radian frequency in radians per second, and 8 is
the phase angle in radians. The sinusoidal signal x(t) is shown in Fig. 1-9, and it is periodic
with fundamental period
The reciprocal of the fundamental period To is called the fundamental frequency fo:
fo=- h ertz (Hz)
7.0
From Eqs. (1.38) and (1.39) we have
which is called the fundamental angular frequency. Using Euler's formula, the sinusoidal
signal in Eq. (1.37) can be expressed as
where "Re" denotes "real part of." We also use the notation "Im" to denote "imaginary
part of." Then
Fig. 1-9 Continuous-time sinusoidal signal.