Page 468 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Signals and Systems
P. 468
Appendix C
Review of Complex Numbers
C.l REPRESENTATION OF COMPLEX NUMBERS
The complex number z can be expressed in several ways.
Cartesian or rectangular form:
z=a+jb
where j = and a and b are real numbers referred to the real part and the imaginary
part of z. a and b are often expressed as
a = Re{z) b = lrn{z) (c.2)
where "Re" denotes the "real part of' and "Im" denotes the "imaginary part of."
Polar form:
z =
where r > 0 is the magnitude of z and 6 is the angle or phasc~ of z. These quantities are
often written as
r = IzI O=LZ (C-4)
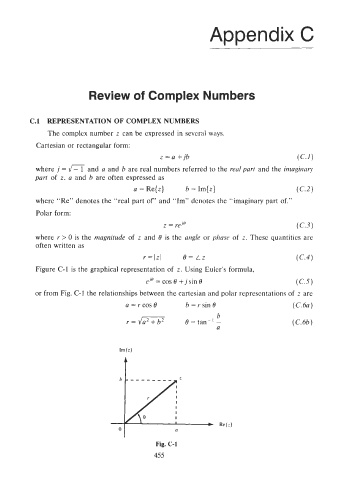
Figure C-1 is the graphical representation of z. Using Euler's formula,
= cos6 +jsinO
(C.5)
or from Fig. C-1 the relationships between the cartesian and polar representations of z are
a = r cos 6 b = I- sin 0 (C.6a)
Fig. C-1
455