Page 275 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 275
264 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY [CHAP. 18
other by a double bond and also be bonded to two hydrogen atoms each.
H H
H C CC H CH 2 CH 2
(b) The line formula CH 3 COCH 3 implies that two of the three carbon atoms each has three hydrogen atoms
attached. This permits them to form one additional single bond, to the middle carbon atom. The middle carbon
atom, with two single bonds to carbon atoms, must complete its total bond order of 4 with a double bond to the
oxygen atom.
H O H O
H C C C H CH 3 C CH 3
H H
18.4. HYDROCARBONS
Compounds consisting of only carbon and hydrogen have the simplest compositions of all organic com-
pounds. These compounds are called hydrocarbons. It is possible to classify the hydrocarbons into series, based
on the characteristic structures of the molecules in each series. The four most fundamental series are known as
the (1) alkane series, (2) alkene series, (3) alkyne series, and (4) aromatic series. There are many subdivisions of
each series, and it is also possible to have molecules that could be classified as belonging to more than one series.
Saturated Hydrocarbons
The alkane series is also called the saturated hydrocarbon series because the molecules of this class have
carbon atoms connected by single bonds only, and therefore have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms
possible for the number of carbon atoms. These substances may be represented by the general formula C n H 2n+2 ,
and molecules of successive members of the series differ from each other by only a CH 2 unit. The line formulas
and names of the first 10 unbranched members of the series, given in Table 18-2, should be memorized because
these names form the basis for naming many other organic compounds. Note that the first parts of the names
of the later members listed are the Greek or Latin prefixes that denote the number of carbon atoms. Also note
that the characteristic ending of each name is -ane. Names of other organic compounds are derived from these
names by dropping the -ane ending and adding other endings. At room temperature, the first four members of
this series are gases; the remainder of those listed in Table 18-2 are liquids. Members of the series having more
than 13 carbon atoms are solids at room temperature.
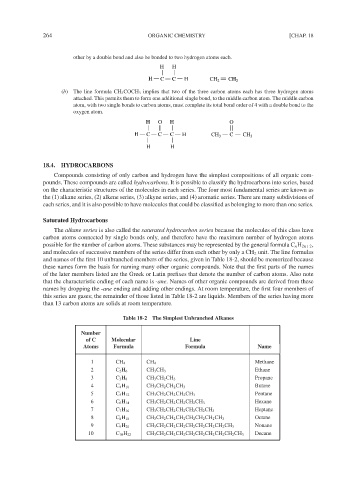
Table 18-2 The Simplest Unbranched Alkanes
Number
of C Molecular Line
Atoms Formula Formula Name
1 CH 4 CH 4 Methane
2 C 2 H 6 CH 3 CH 3 Ethane
3 C 3 H 8 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 Propane
4 C 4 H 10 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 Butane
5 C 5 H 12 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 Pentane
6 C 6 H 14 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 Hexane
7 C 7 H 16 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 Heptane
8 C 8 H 18 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 Octane
9 C 9 H 20 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 Nonane
10 C 10 H 22 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 Decane