Page 277 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 277
266 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY [CHAP. 18
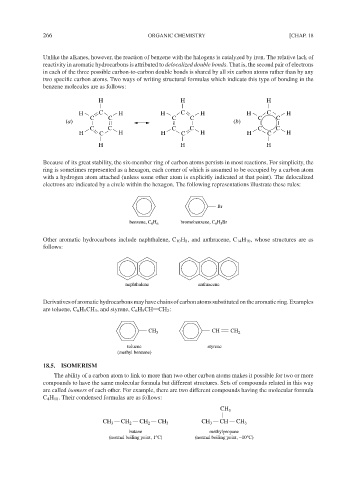
Unlike the alkanes, however, the reaction of benzene with the halogens is catalyzed by iron. The relative lack of
reactivity in aromatic hydrocarbons is attributed to delocalized double bonds. That is, the second pair of electrons
in each of the three possible carbon-to-carbon double bonds is shared by all six carbon atoms rather than by any
two specific carbon atoms. Two ways of writing structural formulas which indicate this type of bonding in the
benzene molecules are as follows:
H H H
H C H H C H H C H
C C C C C C
(a) (b)
C C C C C C
H C H H C H H C H
H H H
Because of its great stability, the six-member ring of carbon atoms persists in most reactions. For simplicity, the
ring is sometimes represented as a hexagon, each corner of which is assumed to be occupied by a carbon atom
with a hydrogen atom attached (unless some other atom is explicitly indicated at that point). The delocalized
electrons are indicated by a circle within the hexagon. The following representations illustrate these rules:
Br
benzene, C H bromobenzene, C 6 5
H Br
6 6
Other aromatic hydrocarbons include naphthalene, C 10 H 8 , and anthracene, C 14 H 10 , whose structures are as
follows:
naphthalene anthracene
Derivativesofaromatichydrocarbonsmayhavechainsofcarbonatomssubstitutedonthearomaticring.Examples
are toluene, C 6 H 5 CH 3 , and styrene, C 6 H 5 CH CH 2 :
CH 3 CH CH 2
toluene styrene
(methyl benzene)
18.5. ISOMERISM
The ability of a carbon atom to link to more than two other carbon atoms makes it possible for two or more
compounds to have the same molecular formula but different structures. Sets of compounds related in this way
are called isomers of each other. For example, there are two different compounds having the molecular formula
C 4 H 10 . Their condensed formulas are as follows:
CH 3
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 3
butane methylpropane
(normal boiling point, 1°C) (normal boiling point, −10°C)