Page 281 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 281
270 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY [CHAP. 18
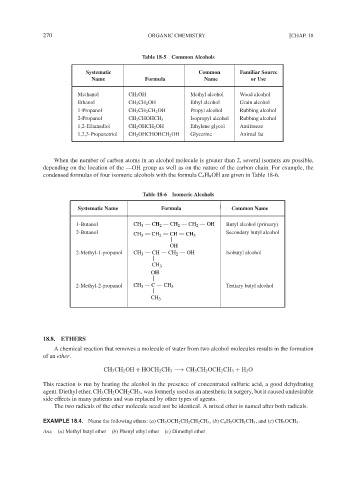
Table 18-5 Common Alcohols
Systematic Common Familiar Source
Name Formula Name or Use
Methanol CH 3 OH Methyl alcohol Wood alcohol
Ethanol CH 3 CH 2 OH Ethyl alcohol Grain alcohol
1-Propanol CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH Propyl alcohol Rubbing alcohol
2-Propanol CH 3 CHOHCH 3 Isopropyl alcohol Rubbing alcohol
1,2-Ethanediol CH 2 OHCH 2 OH Ethylene glycol Antifreeze
1,2,3-Propanetriol CH 2 OHCHOHCH 2 OH Glycerine Animal fat
When the number of carbon atoms in an alcohol molecule is greater than 2, several isomers are possible,
depending on the location of the —OH group as well as on the nature of the carbon chain. For example, the
condensed formulas of four isomeric alcohols with the formula C 4 H 9 OH are given in Table 18-6.
Table 18-6 Isomeric Alcohols
Systematic Name Formula Common Name
1-Butanol CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 OH Butyl alcohol (primary)
2-Butanol CH 3 CH 2 CH CH 3 Secondary butyl alcohol
OH
2-Methyl-1-propanol CH 3 CH CH 2 OH Isobutyl alcohol
CH 3
OH
2-Methyl-2-propanol CH 3 C CH 3 Tertiary butyl alcohol
CH 3
18.8. ETHERS
A chemical reaction that removes a molecule of water from two alcohol molecules results in the formation
of an ether.
CH 3 CH 2 OH + HOCH 2 CH 3 −→ CH 3 CH 2 OCH 2 CH 3 + H 2 O
This reaction is run by heating the alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, a good dehydrating
agent. Diethyl ether, CH 3 CH 2 OCH 2 CH 3 , was formerly used as an anesthetic in surgery, but it caused undesirable
side effects in many patients and was replaced by other types of agents.
The two radicals of the ether molecule need not be identical. A mixed ether is named after both radicals.
EXAMPLE 18.4. Name the following ethers: (a)CH 3 OCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 ,(b)C 6 H 5 OCH 2 CH 3 , and (c)CH 3 OCH 3 .
Ans. (a) Methyl butyl ether (b) Phenyl ethyl ether (c) Dimethyl ether