Page 286 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 286
CHAP. 18] ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 275
18.17. Condensed formulas for C 3 H 8 and C 2 H 4 are fairly easy to write. Explain why they would be harder to
write for C 4 H 10 and C 3 H 6 .
Ans. These compounds can each form isomers (having the same molecular formulas). C 4 H 10 can occur as an
unbranched compound and a branched-chain compound. C 3 H 6 can occur with a double bond or in a ring.
18.18. Explainwhytherecanbenotwo-carbonbranchinanalkanethatcontainsafour-carbonlongestcontinuous
chain.
Ans. A branch cannot start at the end of a carbon chain, and so it must be from one of the two center carbon
atoms in the parent compound. If a two-carbon chain is added there, the two-carbon chain becomes part of
the longest chain, and a one-carbon side chain is left.
C
longest chain
C
Side chain C C C C
18.19. Draw condensed formulas to represent the two isomers of butene which contain no branches.
Ans. CH 3 CH 2 CH CH 2 CH 3 CH CH CH 3
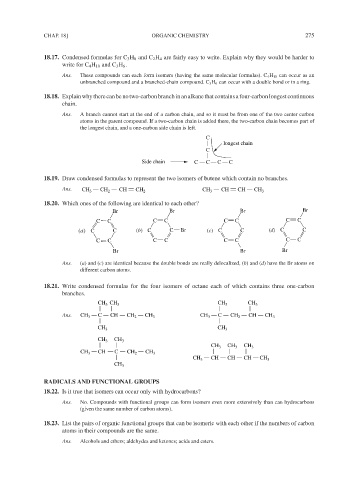
18.20. Which ones of the following are identical to each other?
Br Br Br Br
C C C C C C C C
(a) C C (b) C C Br (c) C C (d) C C
C C C C C C C C
Br Br Br
Ans. (a) and (c) are identical because the double bonds are really delocalized, (b) and (d) have the Br atoms on
different carbon atoms.
18.21. Write condensed formulas for the four isomers of octane each of which contains three one-carbon
branches.
CH CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
3
Ans. CH 3 C CH CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 C CH 2 CH CH 3
CH 3 CH 3
CH 3 CH 3
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
CH 3 CH C CH 2 CH 3
CH 3 CH CH CH CH 3
CH 3
RADICALS AND FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
18.22. Is it true that isomers can occur only with hydrocarbons?
Ans. No. Compounds with functional groups can form isomers even more extensively than can hydrocarbons
(given the same number of carbon atoms).
18.23. List the pairs of organic functional groups that can be isomeric with each other if the numbers of carbon
atoms in their compounds are the same.
Ans. Alcohols and ethers; aldehydes and ketones; acids and esters.