Page 285 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 285
274 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY [CHAP. 18
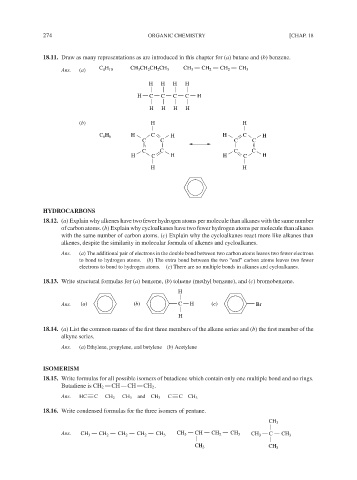
18.11. Draw as many representations as are introduced in this chapter for (a) butane and (b) benzene.
C H CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH
Ans. (a) 4 10 3 2 2 3 3 2 2 3
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H H H
(b) H H
H
C 6 6 H C H H C H
C C C C
C C C C
H C H H C H
H H
HYDROCARBONS
18.12. (a) Explain why alkenes have two fewer hydrogen atoms per molecule than alkanes with the same number
of carbon atoms. (b) Explain why cycloalkanes have two fewer hydrogen atoms per molecule than alkanes
with the same number of carbon atoms. (c) Explain why the cycloalkanes react more like alkanes than
alkenes, despite the similarity in molecular formula of alkenes and cycloalkanes.
Ans. (a) The additional pair of electrons in the double bond between two carbon atoms leaves two fewer electrons
to bond to hydrogen atoms. (b) The extra bond between the two “end” carbon atoms leaves two fewer
electrons to bond to hydrogen atoms. (c) There are no multiple bonds in alkanes and cycloalkanes.
18.13. Write structural formulas for (a) benzene, (b) toluene (methyl benzene), and (c) bromobenzene.
H
Ans. (a) (b) C H (c) Br
H
18.14. (a) List the common names of the first three members of the alkene series and (b) the first member of the
alkyne series.
Ans. (a) Ethylene, propylene, and butylene (b) Acetylene
ISOMERISM
18.15. Write formulas for all possible isomers of butadiene which contain only one multiple bond and no rings.
CH CH CH 2 .
Butadiene is CH 2
Ans. HC C CH 2 CH 3 and CH 3 C C CH 3
18.16. Write condensed formulas for the three isomers of pentane.
CH 3
Ans. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 CH 3 CH 3 C CH 3
CH 3 CH 3