Page 325 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 325
282
Cha p te r
S i x
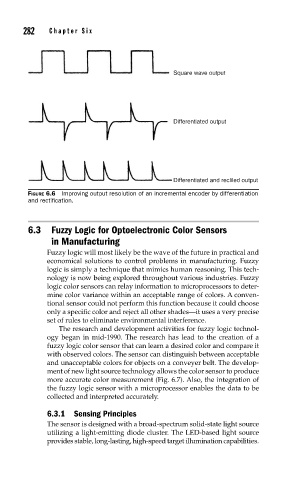
Square wave output
Differentiated output
Differentiated and recliled output
FIGURE 6.6 Improving output resolution of an incremental encoder by differentiation
and rectifi cation.
6.3 Fuzzy Logic for Optoelectronic Color Sensors
in Manufacturing
Fuzzy logic will most likely be the wave of the future in practical and
economical solutions to control problems in manufacturing. Fuzzy
logic is simply a technique that mimics human reasoning. This tech-
nology is now being explored throughout various industries. Fuzzy
logic color sensors can relay information to microprocessors to deter-
mine color variance within an acceptable range of colors. A conven-
tional sensor could not perform this function because it could choose
only a specific color and reject all other shades—it uses a very precise
set of rules to eliminate environmental interference.
The research and development activities for fuzzy logic technol-
ogy began in mid-1990. The research has lead to the creation of a
fuzzy logic color sensor that can learn a desired color and compare it
with observed colors. The sensor can distinguish between acceptable
and unacceptable colors for objects on a conveyer belt. The develop-
ment of new light source technology allows the color sensor to produce
more accurate color measurement (Fig. 6.7). Also, the integration of
the fuzzy logic sensor with a microprocessor enables the data to be
collected and interpreted accurately.
6.3.1 Sensing Principles
The sensor is designed with a broad-spectrum solid-state light source
utilizing a light-emitting diode cluster. The LED-based light source
provides stable, long-lasting, high-speed target illumination capabilities.