Page 92 - Separation process engineering
P. 92
where the damping factor d is about 0.5. Note that when d = 1.0, this is just the Newtonian approach.
The drum temperature should always lie between the bubble- and dew-point temperature of the feed. In
addition, the temperature should converge toward some central value. If either of these criteria is
violated, then the convergence scheme should be damped or an alternative convergence scheme should be
used.
Example 2-3. Simultaneous solution for flash distillation
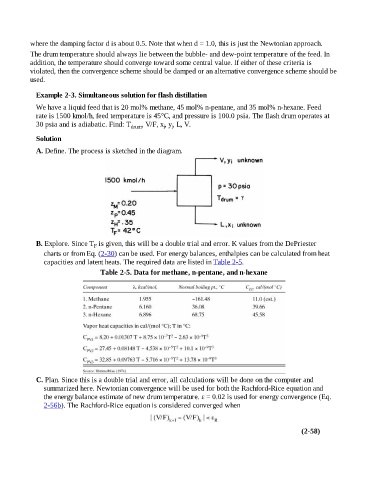
We have a liquid feed that is 20 mol% methane, 45 mol% n-pentane, and 35 mol% n-hexane. Feed
rate is 1500 kmol/h, feed temperature is 45°C, and pressure is 100.0 psia. The flash drum operates at
30 psia and is adiabatic. Find: T drum , V/F, x, y, L, V.
i
i
Solution
A. Define. The process is sketched in the diagram.
B. Explore. Since T is given, this will be a double trial and error. K values from the DePriester
F
charts or from Eq. (2-30) can be used. For energy balances, enthalpies can be calculated from heat
capacities and latent heats. The required data are listed in Table 2-5.
Table 2-5. Data for methane, n-pentane, and n-hexane
C. Plan. Since this is a double trial and error, all calculations will be done on the computer and
summarized here. Newtonian convergence will be used for both the Rachford-Rice equation and
the energy balance estimate of new drum temperature. ε = 0.02 is used for energy convergence (Eq.
2-56b). The Rachford-Rice equation is considered converged when
(2-58)