Page 178 -
P. 178
9 Verifying and Validating Simulations 175
9.2 The Simulation Development Process
Several chains of intermediate models are developed before obtaining a satisfactory
verified and validated model. What does it mean to verify and validate a model
in social simulation? Is there a fundamental difference between verifying and
validating models? The purpose of this section is to define the role of V&V within
the scope of the simulation development process.
The most common definitions of V&V are imported from computer science,
1
as well as from technical and numerical simulation, having intended distinct—
although epistemologically overlapping—meanings. The reason for distinguishing
between the terms derives from the practice of determining the suitability of certain
models for representing two distinct subjects of inquiry. This is represented in
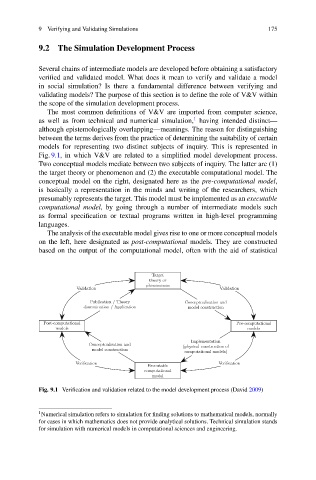
Fig. 9.1, in which V&V are related to a simplified model development process.
Two conceptual models mediate between two subjects of inquiry. The latter are (1)
the target theory or phenomenon and (2) the executable computational model. The
conceptual model on the right, designated here as the pre-computational model,
is basically a representation in the minds and writing of the researchers, which
presumably represents the target. This model must be implemented as an executable
computational model, by going through a number of intermediate models such
as formal specification or textual programs written in high-level programming
languages.
The analysis of the executable model gives rise to one or more conceptual models
on the left, here designated as post-computational models. They are constructed
based on the output of the computational model, often with the aid of statistical
Target
theory or
phenomenon
Validation Validation
Publication / Theory Conceptualisation and
dissemination / Application model construction
Post-computational Pre-computational
models models
Implementation
Conceptualisation and (physical construction of
model construction
computational models)
Verification Verification
Executable
computational
model
Fig. 9.1 Verification and validation related to the model development process (David 2009)
1
Numerical simulation refers to simulation for finding solutions to mathematical models, normally
for cases in which mathematics does not provide analytical solutions. Technical simulation stands
for simulation with numerical models in computational sciences and engineering.