Page 174 -
P. 174
6.3 Architectural patterns 157
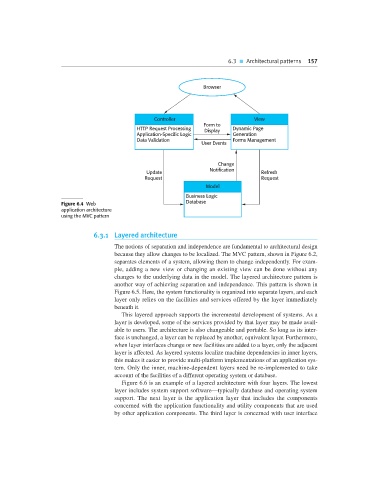
Browser
Controller View
Form to
HTTP Request Processing Display Dynamic Page
Application-Specific Logic Generation
Data Validation Forms Management
User Events
Change
Notification
Update Refresh
Request Request
Model
Business Logic
Database
Figure 6.4 Web
application architecture
using the MVC pattern
6.3.1 Layered architecture
The notions of separation and independence are fundamental to architectural design
because they allow changes to be localized. The MVC pattern, shown in Figure 6.2,
separates elements of a system, allowing them to change independently. For exam-
ple, adding a new view or changing an existing view can be done without any
changes to the underlying data in the model. The layered architecture pattern is
another way of achieving separation and independence. This pattern is shown in
Figure 6.5. Here, the system functionality is organized into separate layers, and each
layer only relies on the facilities and services offered by the layer immediately
beneath it.
This layered approach supports the incremental development of systems. As a
layer is developed, some of the services provided by that layer may be made avail-
able to users. The architecture is also changeable and portable. So long as its inter-
face is unchanged, a layer can be replaced by another, equivalent layer. Furthermore,
when layer interfaces change or new facilities are added to a layer, only the adjacent
layer is affected. As layered systems localize machine dependencies in inner layers,
this makes it easier to provide multi-platform implementations of an application sys-
tem. Only the inner, machine-dependent layers need be re-implemented to take
account of the facilities of a different operating system or database.
Figure 6.6 is an example of a layered architecture with four layers. The lowest
layer includes system support software—typically database and operating system
support. The next layer is the application layer that includes the components
concerned with the application functionality and utility components that are used
by other application components. The third layer is concerned with user interface