Page 179 -
P. 179
162 Chapter 6 Architectural design
Client 1 Client 2 Client 3 Client 4
Internet
Catalogue Video Picture Web
Server Server Server Server
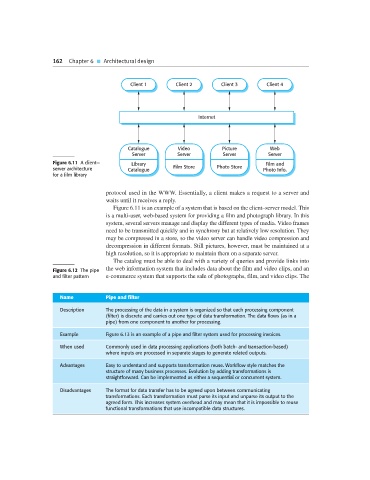
Figure 6.11 A client— Library Film and
server architecture Catalogue Film Store Photo Store Photo Info.
for a film library
protocol used in the WWW. Essentially, a client makes a request to a server and
waits until it receives a reply.
Figure 6.11 is an example of a system that is based on the client–server model. This
is a multi-user, web-based system for providing a film and photograph library. In this
system, several servers manage and display the different types of media. Video frames
need to be transmitted quickly and in synchrony but at relatively low resolution. They
may be compressed in a store, so the video server can handle video compression and
decompression in different formats. Still pictures, however, must be maintained at a
high resolution, so it is appropriate to maintain them on a separate server.
The catalog must be able to deal with a variety of queries and provide links into
Figure 6.12 The pipe the web information system that includes data about the film and video clips, and an
and filter pattern e-commerce system that supports the sale of photographs, film, and video clips. The
Name Pipe and filter
Description The processing of the data in a system is organized so that each processing component
(filter) is discrete and carries out one type of data transformation. The data flows (as in a
pipe) from one component to another for processing.
Example Figure 6.13 is an example of a pipe and filter system used for processing invoices.
When used Commonly used in data processing applications (both batch- and transaction-based)
where inputs are processed in separate stages to generate related outputs.
Advantages Easy to understand and supports transformation reuse. Workflow style matches the
structure of many business processes. Evolution by adding transformations is
straightforward. Can be implemented as either a sequential or concurrent system.
Disadvantages The format for data transfer has to be agreed upon between communicating
transformations. Each transformation must parse its input and unparse its output to the
agreed form. This increases system overhead and may mean that it is impossible to reuse
functional transformations that use incompatible data structures.