Page 291 -
P. 291
274 Chapter 10 Sociotechnical systems
Procurement
Equipment and
software updates
Development
System
Deployment
evolution
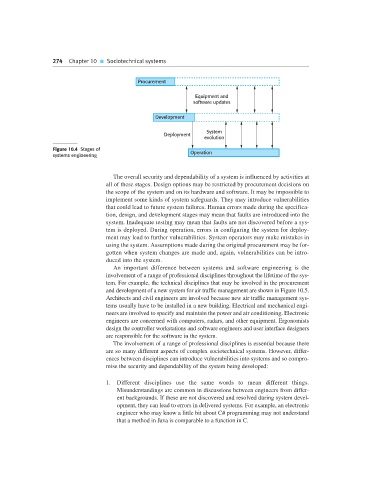
Figure 10.4 Stages of Operation
systems engineering
The overall security and dependability of a system is influenced by activities at
all of these stages. Design options may be restricted by procurement decisions on
the scope of the system and on its hardware and software. It may be impossible to
implement some kinds of system safeguards. They may introduce vulnerabilities
that could lead to future system failures. Human errors made during the specifica-
tion, design, and development stages may mean that faults are introduced into the
system. Inadequate testing may mean that faults are not discovered before a sys-
tem is deployed. During operation, errors in configuring the system for deploy-
ment may lead to further vulnerabilities. System operators may make mistakes in
using the system. Assumptions made during the original procurement may be for-
gotten when system changes are made and, again, vulnerabilities can be intro-
duced into the system.
An important difference between systems and software engineering is the
involvement of a range of professional disciplines throughout the lifetime of the sys-
tem. For example, the technical disciplines that may be involved in the procurement
and development of a new system for air traffic management are shown in Figure 10.5.
Architects and civil engineers are involved because new air traffic management sys-
tems usually have to be installed in a new building. Electrical and mechanical engi-
neers are involved to specify and maintain the power and air conditioning. Electronic
engineers are concerned with computers, radars, and other equipment. Ergonomists
design the controller workstations and software engineers and user interface designers
are responsible for the software in the system.
The involvement of a range of professional disciplines is essential because there
are so many different aspects of complex sociotechnical systems. However, differ-
ences between disciplines can introduce vulnerabilities into systems and so compro-
mise the security and dependability of the system being developed:
1. Different disciplines use the same words to mean different things.
Misunderstandings are common in discussions between engineers from differ-
ent backgrounds. If these are not discovered and resolved during system devel-
opment, they can lead to errors in delivered systems. For example, an electronic
engineer who may know a little bit about C# programming may not understand
that a method in Java is comparable to a function in C.