Page 174 - Soil Degradation, Conservation and Remediation
P. 174
6.2 Sources of Soil Pollutants 163
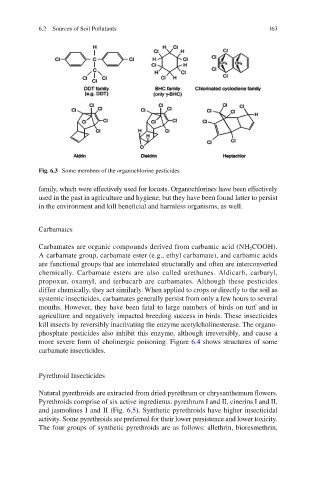
Fig. 6.3 Some members of the organochlorine pesticides
family, which were effectively used for locusts. Organochlorines have been effectively
used in the past in agriculture and hygiene, but they have been found latter to persist
in the environment and kill beneficial and harmless organisms, as well.
Carbamates
Carbamates are organic compounds derived from carbamic acid (NH 2 COOH).
A carbamate group, carbamate ester (e.g., ethyl carbamate), and carbamic acids
are functional groups that are interrelated structurally and often are interconverted
chemically. Carbamate esters are also called urethanes. Aldicarb, carbaryl,
propoxur, oxamyl, and terbucarb are carbamates. Although these pesticides
differ chemically, they act similarly. When applied to crops or directly to the soil as
systemic insecticides, carbamates generally persist from only a few hours to several
months. However, they have been fatal to large numbers of birds on turf and in
agriculture and negatively impacted breeding success in birds. These insecticides
kill insects by reversibly inactivating the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. The organo-
phosphate pesticides also inhibit this enzyme, although irreversibly, and cause a
more severe form of cholinergic poisoning. Figure 6.4 shows structures of some
carbamate insecticides.
Pyrethroid Insecticides
Natural pyrethroids are extracted from dried pyrethrum or chrysanthemum fl owers.
Pyrethroids comprise of six active ingredients: pyrethrum I and II, cinerins I and II,
and jasmolines I and II (Fig. 6.5 ). Synthetic pyrethroids have higher insecticidal
activity. Some pyrethroids are preferred for their lower persistence and lower toxicity.
The four groups of synthetic pyrethroids are as follows: allethrin, bioresmethrin,