Page 177 - Soil Degradation, Conservation and Remediation
P. 177
166 6 Soil Pollution
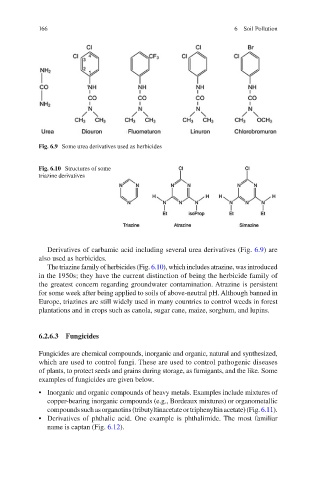
Fig. 6.9 Some urea derivatives used as herbicides
Fig. 6.10 Structures of some
triazine derivatives
Derivatives of carbamic acid including several urea derivatives (Fig. 6.9 ) are
also used as herbicides.
The triazine family of herbicides (Fig. 6.10 ), which includes atrazine, was introduced
in the 1950s; they have the current distinction of being the herbicide family of
the greatest concern regarding groundwater contamination. Atrazine is persistent
for some week after being applied to soils of above-neutral pH. Although banned in
Europe, triazines are still widely used in many countries to control weeds in forest
plantations and in crops such as canola, sugar cane, maize, sorghum, and lupins.
6.2.6.3 Fungicides
Fungicides are chemical compounds, inorganic and organic, natural and synthesized,
which are used to control fungi. These are used to control pathogenic diseases
of plants, to protect seeds and grains during storage, as fumigants, and the like. Some
examples of fungicides are given below.
• Inorganic and organic compounds of heavy metals. Examples include mixtures of
copper-bearing inorganic compounds (e.g., Bordeaux mixtures) or organometallic
compounds such as organotins (tributyltinacetate or triphenyltin acetate) (Fig. 6.11 ).
• Derivatives of phthalic acid. One example is phthalimide. The most familiar
name is captan (Fig. 6.12 ).